Vue v2.6.11 模板编译源码解析
注:建议学习源码从易到难(学习react也可建议先学习react16),核心是感受框架设计的理念,学习vue2后,再去对照学习vue3,从中对比效果更好。
github源码地址:
https://github.com/vuejs/vue/tree/v2.6.11
源码学习路线(红色是重点了解模块)
-
响应式实现篇
学习Vue中如何实现数据的响应式系统,从而达到数据驱动视图
-
虚拟 DOM 篇
学习什么是虚拟 DOM,以及Vue中的DOM-Diff原理
-
模板编译篇
学习Vue内部是怎么把template模板编译成虚拟DOM,从而渲染出真实DOM
-
实例方法篇
学习Vue中所有实例方法(即所有以$开头的方法)的实现原理
-
全局 API 篇
学习Vue中所有全局API的实现原理
-
生命周期篇
学习Vue中组件的生命周期实现原理
-
指令篇
学习Vue中所有指令的实现原理
-
过滤器篇
学习Vue中所有过滤器的实现原理
-
内置组件篇
学习Vue中内置组件的实现原理
项目目录:complier 和 core 是核心
├─dist # 项目构建后的文件├─scripts # 与项目构建相关的脚本和配置文件├─flow # flow的类型声明文件├─src # 项目源代码│ ├─complier # 与模板编译相关的代码│ ├─core # 通用的、与运行平台无关的运行时代码│ │ ├─observe # 实现变化侦测的代码│ │ ├─vdom # 实现virtual dom的代码│ │ ├─instance # Vue.js实例的构造函数和原型方法│ │ ├─global-api # 全局api的代码│ │ └─components # 内置组件的代码│ ├─server # 与服务端渲染相关的代码│ ├─platforms # 特定运行平台的代码,如weex│ ├─sfc # 单文件组件的解析代码│ └─shared # 项目公用的工具代码└─test # 项目测试代码
模版编译
<template><div @click=handleClick>{{ count }}</div><span></span></template>
渲染流程
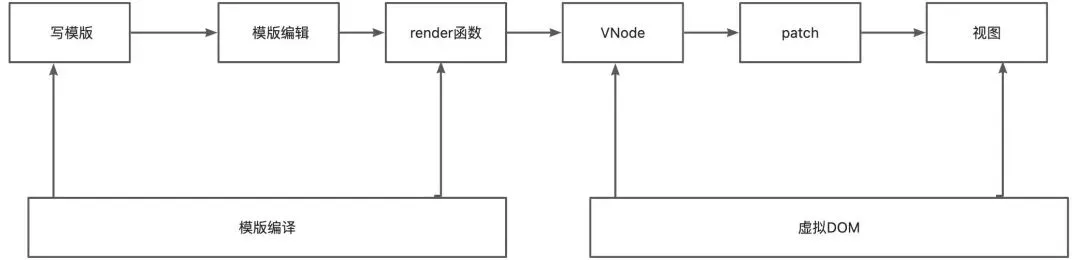
模版解析流程
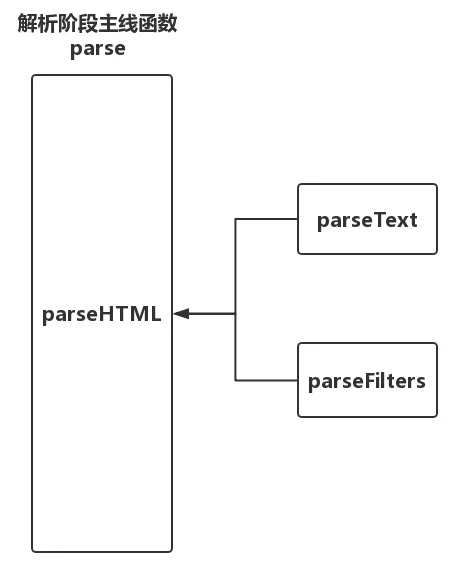
模板解析阶段主要做的工作是把用户在<template></template>标签内写的模板使用正则等方式解析成抽象语法树(AST)。而这一阶段在源码中对应解析器(parser)模块。
解析器,顾名思义,就是把用户所写的模板根据一定的解析规则解析出有效的信息,最后用这些信息形成AST。我们知道在<template></template>模板内,除了有常规的HTML标签外,用户还会一些文本信息以及在文本信息中包含过滤器。而这些不同的内容在解析起来时肯定需要不同的解析规则,所以解析器不可能只有一个,它应该除了有解析常规HTML的HTML解析器,还应该有解析文本的文本解析器以及解析文本中如果包含过滤器的过滤器解析器。
另外,文本信息和标签属性信息却又是存在于HTML标签之内的,所以在解析整个模板的时候它的流程应该是这样子的:HTML解析器是主线,先用HTML解析器进行解析整个模板,在解析过程中如果碰到文本内容,那就调用文本解析器来解析文本,如果碰到文本中包含过滤器那就调用过滤器解析器来解析。如下图所示:
export const createCompiler = createCompilerCreator(function baseCompile (template: string,options: CompilerOptions): CompiledResult {// parse会用正则等方式解析template模版中的指令、class、style等数据,生成ASTconst ast = parse(template.trim(), options)// optimize作用是标记静态节点,在patch的过程中,DOM-DIFF算法会直接跳过静态节点,提高patch性能if (options.optimize !== false) {optimize(ast, options)}// 把AST转换成render函数字符串的过程,得到的是render函数的字符串以及staticRenderFns字符串const code = generate(ast, options)return {ast,render: code.render,staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns}})
function isStatic (node: ASTNode): boolean {if (node.type === 2) { // expressionreturn false}if (node.type === 3) { // textreturn true}return !!(node.pre || (!node.hasBindings && // no dynamic bindings!node.if && !node.for && // not v-if or v-for or v-else!isBuiltInTag(node.tag) && // not a built-inisPlatformReservedTag(node.tag) && // not a component!isDirectChildOfTemplateFor(node) &&Object.keys(node).every(isStaticKey)))}
function markStatic (node: ASTNode) {node.static = isStatic(node)if (node.type === 1) {// do not make component slot content static. this avoids// 1. components not able to mutate slot nodes// 2. static slot content fails for hot-reloadingif (!isPlatformReservedTag(node.tag) &&node.tag !== 'slot' &&node.attrsMap['inline-template'] == null) {return}for (let i = 0, l = node.children.length; i < l; i++) {const child = node.children[i]markStatic(child)if (!child.static) {node.static = false}}if (node.ifConditions) {for (let i = 1, l = node.ifConditions.length; i < l; i++) {const block = node.ifConditions[i].blockmarkStatic(block)if (!block.static) {node.static = false}}}}}
-
type为1:元素节点
-
type为2:包含变量的动态文本节点
-
type为3:不包含变量的纯文本节点
判断静态节点后,需要给静态节点标记
function markStaticRoots (node: ASTNode, isInFor: boolean) {if (node.type === 1) {if (node.static || node.once) {node.staticInFor = isInFor}// For a node to qualify as a static root, it should have children that// are not just static text. Otherwise the cost of hoisting out will// outweigh the benefits and it's better off to just always render it fresh.if (node.static && node.children.length && !(node.children.length === 1 &&node.children[0].type === 3)) {node.staticRoot = truereturn} else {node.staticRoot = false}if (node.children) {for (let i = 0, l = node.children.length; i < l; i++) {markStaticRoots(node.children[i], isInFor || !!node.for)}}if (node.ifConditions) {for (let i = 1, l = node.ifConditions.length; i < l; i++) {markStaticRoots(node.ifConditions[i].block, isInFor)}}}}
HTML解析器
源码位置:src/compiler/parser/index.js line79
parseHTML() {// 解析到开始标签时,调用这个函数,生成元素节点的ASTstart(tag, attrs, unary) {let element: ASTElement = createASTElement(tag, attrs, currentParent)}// 解析到结束标签,调用end函数end(tag, start, end){closeElement(element)}// 解析到文本时,调用chars函数生成文本类型的ast节点chars(text) {// 如果是带变量的动态文本if (!inVPre && text !== ' ' && (res = parseText(text, delimiters))) {child = {type: 2,expression: res.expression,tokens: res.tokens,text}} else if (text !== ' ' || !children.length || children[children.length - 1].text !== ' ') {child = {type: 3,text}}}// 当解析到标签的注释,触发commentcomment(text) {const child: ASTText = {type: 3,text,isComment: true}}}
-
文本
-
HTML注释 <!– 注释–>
-
条件注释 <!– [if !!IE]>
const comment = /^<!\--/if (comment.test(html)) {const commentEnd = html.indexOf('-->')if (commentEnd >= 0) {if (options.shouldKeepComment) {options.comment(html.substring(4, commentEnd), index, index + commentEnd + 3)}// 移动解析游标/*index 0advance(3)index 3 (v)<div >{{ greeting }} World!</div>*/advance(commentEnd + 3)continue}}
-
开始标签,比如 <div>
functionparseStartTag() {const startTagOpen = new RegExp(`^<${qnameCapture}`)const start = html.match(startTagOpen)if (start) {const match = {tagName: start[1],attrs: [],start: index}advance(start[0].length)let end, attrwhile (!(end = html.match(startTagClose)) && (attr = html.match(dynamicArgAttribute) || html.match(attribute))) {attr.start = indexadvance(attr[0].length)attr.end = indexmatch.attrs.push(attr)}if (end) {match.unarySlash = end[1]advance(end[0].length)match.end = indexreturn match}}}
-
结束标签,比如</div>
如何保证AST节点层级关系
Vue在HTML解析器的开头定义了一个stack栈,这个栈的作用就是维护AST节点层级的
<div><p><span></span></p></div>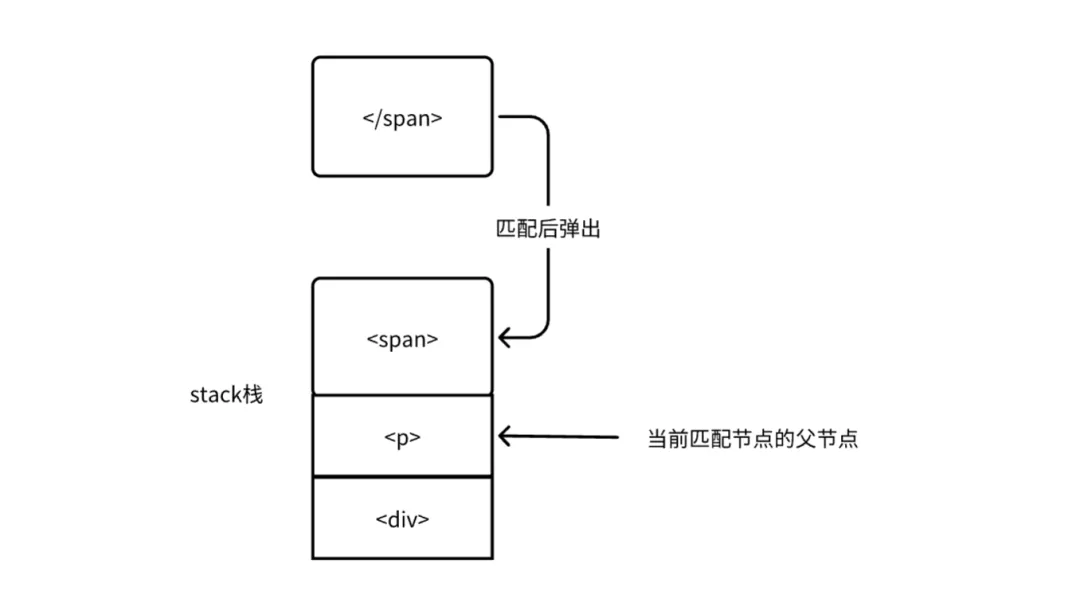
<div><p><span></p></div>这个栈也可以检测模版字符串中是否有未正确闭合的标签
文本解析器
当HTML解析器解析到文本内容时会调用4个钩子函数中的chars函数来创建文本型的AST节点,并且也说了在chars函数中会根据文本内容是否包含变量再细分为创建含有变量的AST节点和不包含变量的AST节点,如下:
var text = ${data} ? 'data' : 'xx';// 当解析到标签的文本时,触发charschars (text) {if(res = parseText(text)){let element = {type: 2,expression: res.expression,tokens: res.tokens,text}} else {let element = {type: 3,text}}}
从上面代码中可以看到,创建含有变量的AST节点时节点的type属性为2,并且相较于不包含变量的AST节点多了两个属性:expression和tokens。那么如何来判断文本里面是否包含变量以及多的那两个属性是什么呢?这就涉及到文本解析器了,当Vue用HTML解析器解析出文本时,再将解析出来的文本内容传给文本解析器,最后由文本解析器解析该段文本里面是否包含变量以及如果包含变量时再解析expression和tokens。
假设我们通过HTML解析器得到这样的文本:
let text = "我叫{{name}}, 我几年{{age}}岁了";let res = parseText(text);res = {expression: "我叫" + _s(name)+ ", 我今年"+ _s(age)+ "岁了",tokens: ["我叫",{'@binding': name},", 我今年",{'@binding': age},"岁了"]}
/* @flow */import { cached } from 'shared/util'import { parseFilters } from './filter-parser'const defaultTagRE = /\{\{((?:.|\r?\n)+?)\}\}/gconst regexEscapeRE = /[-.*+?^${}()|[\]\/\\]/gconst buildRegex = cached(delimiters => {const open = delimiters[0].replace(regexEscapeRE, '\\$&')const close = delimiters[1].replace(regexEscapeRE, '\\$&')return new RegExp(open + '((?:.|\\n)+?)' + close, 'g')})type TextParseResult = {expression: string,tokens: Array<string | { '@binding': string }>}export functionparseText (text: string,delimiters?: [string, string]): TextParseResult | void {// 检测文本是否包含变量 %%hello%%const tagRE = delimiters ? buildRegex(delimiters) : defaultTagREif (!tagRE.test(text)) {return}const tokens = []const rawTokens = []let lastIndex = tagRE.lastIndex = 0let match, index, tokenValue// tagRe.exec("hello {{name}}, I am {{age}}")// 返回["{{name}}", "name", index: 6, input:'xxx']//while ((match = tagRE.exec(text))) {index = match.index// push text tokenif (index > lastIndex) {// 表示变量前面有纯文本rawTokens.push(tokenValue = text.slice(lastIndex, index))tokens.push(JSON.stringify(tokenValue))}// 表示文本一开始就是变量 {{hello}}name// tag tokenconst exp = parseFilters(match[1].trim())tokens.push(_s(${exp}))rawTokens.push({ '@binding': exp })// 更新lastIndex 保证在下一轮循环的时候,只从 }}后边再开始匹配lastIndex = index + match[0].length}// 当剩下的text不再被正则匹配的时候,表示所有变量都已经处理完毕// 此时如果lastIndex < text.length 表示在最后一个变量后还有文本// 最后将后边的文本加入到tokents中if (lastIndex < text.length) {rawTokens.push(tokenValue = text.slice(lastIndex))tokens.push(JSON.stringify(tokenValue))}return {expression: tokens.join('+'),tokens: rawTokens}}
优化阶段
在模板编译的时候就先找出模板中所有的静态节点和静态根节点,然后给它们打上标记,用于告诉后面patch过程打了标记的这些节点是不需要对比,这就是优化阶段。
// ul称为静态根节点<ul><li>文本111</li><li>文本111</li><li>文本111</li><li>文本111</li><li>文本111</li></ul>
-
在
AST中找出所有静态节点并打上标记; -
在
AST中找出所有静态根节点并打上标记;
function markStatic (node: ASTNode) {node.static = isStatic(node)if (node.type === 1) {// do not make component slot content static. this avoids// 1. components not able to mutate slot nodes// 2. static slot content fails for hot-reloadingif (!isPlatformReservedTag(node.tag) &&node.tag !== 'slot' &&node.attrsMap['inline-template'] == null) {return}for (let i = 0, l = node.children.length; i < l; i++) {const child = node.children[i]markStatic(child)// 如果当前节点的子节点有一个不是静态节点,那么就把当前节点也标记为非静态节点//if (!child.static) {node.static = false}}// 如果当前节点的子节点中有标签带有v-if、v-else-if、v-else等指令if (node.ifConditions) {for (let i = 1, l = node.ifConditions.length; i < l; i++) {const block = node.ifConditions[i].blockmarkStatic(block)if (!block.static) {node.static = false}}}}}
function markStaticRoots (node: ASTNode, isInFor: boolean) {if (node.type === 1) {if (node.static || node.once) {node.staticInFor = isInFor}// For a node to qualify as a static root, it should have children that// are not just static text. Otherwise the cost of hoisting out will// outweigh the benefits and it's better off to just always render it fresh.// 一个节点想要成为静态根节点// 节点本身必须是静态节点// 必须要拥有子节点children// 子节点不能是只有一个文本节点if (node.static && node.children.length && !(node.children.length === 1 &&node.children[0].type === 3)) {node.staticRoot = truereturn} else {node.staticRoot = false}if (node.children) {for (let i = 0, l = node.children.length; i < l; i++) {markStaticRoots(node.children[i], isInFor || !!node.for)}}if (node.ifConditions) {for (let i = 1, l = node.ifConditions.length; i < l; i++) {markStaticRoots(node.ifConditions[i].block, isInFor)}}}}
代码生成阶段
所谓代码生成其实就是根据模板对应的抽象语法树AST生成一个函数,通过调用这个函数就可以得到模板对应的虚拟DOM。
-
如何根据AST生成render函数?
假设现有如下模板:
<divid="NLRX"><p>Hello {{name}}</p></div>该模板经过解析并优化后对应的AST如下:
ast = {'type': 1,'tag': 'div','attrsList': [{'name':'id','value':'NLRX',}],'attrsMap': {'id': 'NLRX',},'static':false,'parent': undefined,'plain': false,'children': [{'type': 1,'tag': 'p','plain': false,'static':false,'children': [{'type': 2,'expression': '"Hello "+_s(name)','text': 'Hello {{name}}','static':false,}]}]}
-
首先,根节点div是一个元素类型的AST节点,我们需要创建一个元素类型的VNode。
_c('div', {attrs: {"id": "NLRX"}}, [/*子节点列表*/])-
其次,根节点div具有子节点,那么我们进入子节点列表children遍历子节点,发现子节点p也是元素型,我们就继续创建元素型节点VNode并且将其放入根节点的子节点列表中,如下:
_c('div', {attrs: {"id": "NLRX"}}, [_c('p', {attrs:{}}, [/*子节点列表*/])])-
继续遍历p节点的子节点,发现是一个文本型节点,我们就创建一个文本型VNode并将其插入到p节点的子节点列表中,如下:
_c('div', {attrs: {"id": "NLRX"}}, [_c('p', {attrs:{}}, [_v("Hello"+_s(name))])])-
接着,我们遍历完后,把得到的代码包装一下,如下:
`with(this){return _c('div',{attrs: {"id": "NLRX"},},[_c('p',{attrs: {}},[_v("hello"+_s(name))])])}`
-
最后,我们把上边得到的函数字符串传递给createFunction函数, createFunction会帮我们把得到的字符串转换成真正的函数,赋给组件中的render选型,从而就是render函数了
res.render = createFunction(coplied.render, fnGenErrors)function createFunction(code, errors) {try {return new Function(code)} catch (err) {errors.push({err, code}),return}}
代码生成阶段的源码位于src/complier/codegen/index.js
export function generate (ast: ASTElement | void,options: CompilerOptions): CodegenResult {const state = new CodegenState(options)const code = ast ? genElement(ast, state) : '_c("div")'return {render:with(this){return ${code}},staticRenderFns: state.staticRenderFns}}
genElement函数就是根据当前AST元素节点属性的不同,从而执行不同的代码生成函数。
export function genElement (el: ASTElement, state: CodegenState): string {if (el.parent) {el.pre = el.pre || el.parent.pre}if (el.staticRoot && !el.staticProcessed) {return genStatic(el, state)} else if (el.once && !el.onceProcessed) {return genOnce(el, state)} else if (el.for && !el.forProcessed) {return genFor(el, state)} else if (el.if && !el.ifProcessed) {return genIf(el, state)} else if (el.tag === 'template' && !el.slotTarget && !state.pre) {return genChildren(el, state) || 'void 0'} else if (el.tag === 'slot') {return genSlot(el, state)} else {// component or elementlet codeif (el.component) {code = genComponent(el.component, el, state)} else {let dataif (!el.plain || (el.pre && state.maybeComponent(el))) {data = genData(el, state)}const children = el.inlineTemplate ? null : genChildren(el, state, true)code = _c('${el.tag}'${data ? , ${data}` : '' // data}${children ? ,${children}: '' // children})`}// module transformsfor (let i = 0; i < state.transforms.length; i++) {code = state.transforms[i](el, code)}return code}}
1.元素节点
functiongenNormalElement(el, state, stringifyChildren) {const data = el.plain ? undefined : genData(el, state)const children = stringifyChildren?[${genChildrenAsStringNode(el, state)}]: genSSRChildren(el, state, true)return _c('${el.tag}' ${ data ? , ${data}` : ''}${children ? , ${children} : ''})`}
genData就是在拼接字符串,先给data赋值一个{,然后判断存在哪些属性数据,就把对应的数据拼接到data中,最后再加一个},得到节点全部属性data
2.获取子节点列表children
export function genChildren (el: ASTElement,state: CodegenState,checkSkip?: boolean,altGenElement?: Function,altGenNode?: Function): string | void {const children = el.childrenif (children.length) {const el: any = children[0]// optimize single v-forif (children.length === 1 &&el.for &&el.tag !== 'template' &&el.tag !== 'slot') {const normalizationType = checkSkip ? state.maybeComponent(el) ? ,1:,0 : ``return ${(altGenElement || genElement)(el, state)}${normalizationType}}const normalizationType = checkSkip ? getNormalizationType(children, state.maybeComponent): 0const gen = altGenNode || genNodereturn [${children.map(c =>gen(c, state)).join(',')}]${ normalizationType ? ,${normalizationType}: ''}}}
function genNode (node: ASTNode, state: CodegenState): string {if (node.type === 1) {return genElement(node, state)} else if (node.type === 3 && node.isComment) {return genComment(node)} else {return genText(node)}}
2.文本节点
文本型的调用_v(text)创建
export function genText (text: ASTText | ASTExpression): string {return_v(${text.type===2? text.expression// no need for () because already wrapped in _s() : transformSpecialNewlines(JSON.stringify(text.text)) })}
3.注释节点
注释型的vNode调用_e(text)函数来创建
export function genComment (comment: ASTText): string {return _e(${JSON.stringify(comment.text)})}
总结
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el?: string | Element,hydrating?: boolean): Component {el = el && query(el)/* istanbul ignore if */if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) {process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.)return this}const options = this.$options// resolve template/el and convert to render functionif (!options.render) {let template = options.templateif (template) {if (typeof template === 'string') {if (template.charAt(0) === '#') {template = idToTemplate(template)/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !template) {warn(`Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`,this)}}} else if (template.nodeType) {template = template.innerHTML} else {if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {warn('invalid template option:' + template, this)}return this}} else if (el) {template = getOuterHTML(el)}if (template) {/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {mark('compile')}const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, {outputSourceRange: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',shouldDecodeNewlines,shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,delimiters: options.delimiters,comments: options.comments}, this)options.render = renderoptions.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {mark('compile end')measure(vue ${this._name} compile, 'compile', 'compile end')}}}return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)}
export const createCompiler = createCompilerCreator(function baseCompile (template: string,options: CompilerOptions): CompiledResult {// 模版解析节点,用正则等方式解析template模版中的指令、class、style等数据,生成astconst ast = parse(template.trim(), options)if (options.optimize !== false) {// 第二阶段-优化阶段,遍历AST,找出其中的静态节点,并打上标记optimize(ast, options)}// 第三阶段-代码生成阶段,将AST转换成渲染函数const code = generate(ast, options)return {ast,render: code.render,staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns}})
 夜雨聆风
夜雨聆风





