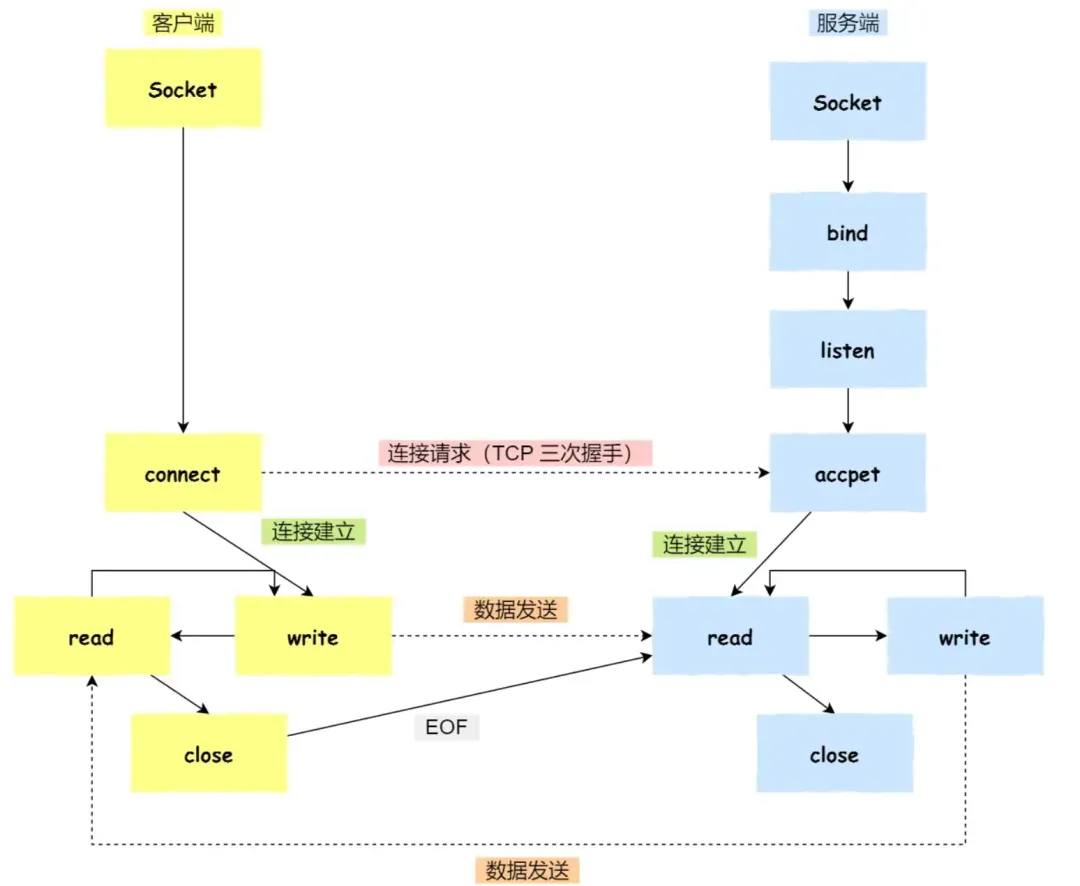
详解Socket状态机源码
系统调用方法
lock_scok()
lock_sock()本质是调用了一次lock_sock_nested(sock, 0) 。
// net/core/sock.c
void lock_sock_nested(struct sock *sk, int subclass)
{
/* The sk_lock has mutex_lock() semantics here. */
mutex_acquire(&sk->sk_lock.dep_map, subclass, 0, _RET_IP_);
might_sleep();
spin_lock_bh(&sk->sk_lock.slock);
if (sock_owned_by_user_nocheck(sk))
__lock_sock(sk);
sk->sk_lock.owned = 1;
spin_unlock_bh(&sk->sk_lock.slock);
}
Listen()
最外层的listen()本质是__sys_listen()方法,在该调用内部启用inet_listen()方法。 在这一层检验监听Socket是否可用。
// include/net/ipv4/af_inet.c
int inet_listen(struct socket *sock, int backlog)
{
struct sock *sk = sock->sk;
int err = -EINVAL;
lock_sock(sk);
if (sock->state != SS_UNCONNECTED || sock->type != SOCK_STREAM)
goto out;
// 下层逻辑调用
err = __inet_listen_sk(sk, backlog);
out:
release_sock(sk);
return err;
}
__inet_listen_sk()则是写入backlog,并且对非TCP_LISTEN状态的Socket,通过inet_csk_listen_start()进行状态流转。
old_state != TCP_LISTEN是用于区分listen()的系统调用是否被重复触发的逻辑。这是因为Linux源码在inet_csk_listen_start()中执行了内存绑定,队列初始化等操作,在初始化一次监听Socket后,防止在之后的listen()中被再次调用强行清空连接队列。
// include/net/ipv4/af_inet.c
int __inet_listen_sk(struct sock *sk, int backlog)
{
unsigned char old_state = sk->sk_state;
int err, tcp_fastopen;
if (!((1 << old_state) & (TCPF_CLOSE | TCPF_LISTEN)))
return -EINVAL;
WRITE_ONCE(sk->sk_max_ack_backlog, backlog);
/* Really, if the socket is already in listen state
* we can only allow the backlog to be adjusted.
*/
if (old_state != TCP_LISTEN) {
/* Enable TFO w/o requiring TCP_FASTOPEN socket option.
* Note that only TCP sockets (SOCK_STREAM) will reach here.
* Also fastopen backlog may already been set via the option
* because the socket was in TCP_LISTEN state previously but
* was shutdown() rather than close().
*/
tcp_fastopen = READ_ONCE(sock_net(sk)->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_fastopen);
if ((tcp_fastopen & TFO_SERVER_WO_SOCKOPT1) &&
(tcp_fastopen & TFO_SERVER_ENABLE) &&
!inet_csk(sk)->icsk_accept_queue.fastopenq.max_qlen) {
fastopen_queue_tune(sk, backlog);
tcp_fastopen_init_key_once(sock_net(sk));
}
err = inet_csk_listen_start(sk);
if (err)
return err;
tcp_call_bpf(sk, BPF_SOCK_OPS_TCP_LISTEN_CB, 0, NULL);
}
return 0;
}
inet_csk_listen_start()是最底层的listen()系统调用实现。内核在这一步主要进行了以下操作:
● 初始化TCP FastOpen队列和全连接队列
● 清空全连接队列的连接计数器
● 切换监听Socket的状态 -> TCP_LISTEN
● 放入listen hash表
listen hash表并不是全局ehash连接表,也不是bhash端口连接表,而是存放所有监听Socket的哈希表。 经过这一步正式将监听Socket注册,这个Socket和对应的端口才算是正式可用。未经过这一步的Socket对操作系统是不可见的。
// net/ipv4/inet_connection_sock.c
int inet_csk_listen_start(struct sock *sk)
{
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
int err;
err = inet_ulp_can_listen(sk);
if (unlikely(err))
return err;
// 初始化 连接队列容器
reqsk_queue_alloc(&icsk->icsk_accept_queue);
// 清空全连接队列元素数量
sk->sk_ack_backlog = 0;
inet_csk_delack_init(sk);
/* There is race window here: we announce ourselves listening,
* but this transition is still not validated by get_port().
* It is OK, because this socket enters to hash table only
* after validation is complete.
*/
// 切换sk状态
inet_sk_state_store(sk, TCP_LISTEN);
// 检查端口号
err = sk->sk_prot->get_port(sk, inet->inet_num);
if (!err) {
inet->inet_sport = htons(inet->inet_num);
// 清除Cache
sk_dst_reset(sk);
// 放入listen hash表
err = sk->sk_prot->hash(sk);
if (likely(!err))
return 0;
}
inet_sk_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSE);
return err;
}
// net/core/request_sock.c
void reqsk_queue_alloc(struct request_sock_queue *queue)
{
// 初始化FastOpen队列
queue->fastopenq.rskq_rst_head = NULL;
queue->fastopenq.rskq_rst_tail = NULL;
queue->fastopenq.qlen = 0;
// 初始化全连接队列
queue->rskq_accept_head = NULL;
}
三次握手 (状态机流转全流程)
初始化TCP Socket
inet_init -> .init = tcp_v4_init_sock()通过 tcp_v4_init_sock() 初始化了一个TCP Socket,提供了一个ipv4_specific接口用于封装TCP协议Socket连接的所有处理。如果是ipv6则会返回一个ipv6_specific。
体现的设计理念: TCP层不感知和区分ipv4还是ipv6,只需调用**ops->function()**,即下面的af_ops
// net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c
static int tcp_v4_init_sock(struct sock *sk)
{
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
tcp_init_sock(sk);
icsk->icsk_af_ops = &ipv4_specific;
#if defined(CONFIG_TCP_MD5SIG) || defined(CONFIG_TCP_AO)
tcp_sk(sk)->af_specific = &tcp_sock_ipv4_specific;
sk->sk_destruct = tcp4_destruct_sock;
#endif
return 0;
}
const struct inet_connection_sock_af_ops ipv4_specific = {
// 发送数据的函数。用于将数据从传输层(TCP)发送到网络层(IP)
.queue_xmit = ip_queue_xmit,
// 用于计算和校验的函数
.send_check = tcp_v4_send_check,
.rebuild_header = inet_sk_rebuild_header,
.sk_rx_dst_set = inet_sk_rx_dst_set,
// 处理SYN段的函数。在TCP三次握手的开始阶段被调用,用于处理来自客户端的SYN包
.conn_request = tcp_v4_conn_request,
// 创建和初始化新socket的函数 在TCP三次握手完成后被调用
.syn_recv_sock = tcp_v4_syn_recv_sock,
.net_header_len = sizeof(struct iphdr),
.setsockopt = ip_setsockopt,
.getsockopt = ip_getsockopt,
.mtu_reduced = tcp_v4_mtu_reduced,
};
服务端
1 · 接收SYN报文
TCP Socket处理第一次SYN请求的方法为tcp_v4_conn_request(),其中调用了tcp_conn_request()方法。
// net/ipv4/tcp_input.c
int tcp_conn_request(struct request_sock_ops *rsk_ops,
const struct tcp_request_sock_ops *af_ops,
struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
...
isn = __this_cpu_read(tcp_tw_isn);
if (isn) {
...
} else {
// SYN-Cookie功能,即使超出半连接队列容量也不会drop连接
syncookies = READ_ONCE(net->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_syncookies);
// inet_csk_reqsk_queue_is_full()判断半连接队列是否满了
if (syncookies == 2 || inet_csk_reqsk_queue_is_full(sk)) {
want_cookie = tcp_syn_flood_action(sk,
rsk_ops->slab_name);
if (!want_cookie)
goto drop;
}
}
// 判断全连接队列是否满了
if (sk_acceptq_is_full(sk)) {
NET_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_LISTENOVERFLOWS);
goto drop;
}
// 创建一个request_sock !!! 核心代码见下文
req = inet_reqsk_alloc(rsk_ops, sk, !want_cookie);
if (!req)
goto drop;
req->syncookie = want_cookie;
tcp_rsk(req)->af_specific = af_ops;
tcp_rsk(req)->ts_off = 0;
tcp_rsk(req)->req_usec_ts = false;
...
// 省略了大量cookie校验逻辑
...
if (fastopen_sk) {
// 发送syn-ack应答报文
af_ops->send_synack(fastopen_sk, dst, &fl, req,
&foc, TCP_SYNACK_FASTOPEN, skb);
// 若SYN-Cookie下的Cookie可信任,则直接入全连接队列
/* Add the child socket directly into the accept queue */
if (!inet_csk_reqsk_queue_add(sk, req, fastopen_sk)) {
bh_unlock_sock(fastopen_sk);
sock_put(fastopen_sk);
goto drop_and_free;
}
//
sk->sk_data_ready(sk);
bh_unlock_sock(fastopen_sk);
sock_put(fastopen_sk);
} else {
tcp_rsk(req)->tfo_listener = false;
if (!want_cookie &&
// 将request_sock添加到半连接队列
unlikely(!inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add(sk, req))) {
reqsk_free(req);
dst_release(dst);
return 0;
}
af_ops->send_synack(sk, dst, &fl, req, &foc,
!want_cookie ? TCP_SYNACK_NORMAL :
TCP_SYNACK_COOKIE,
skb);
...
reqsk_put(req);
return 0;
...
}
// net/ipv4/inet_connection_sock.c
struct request_sock *inet_reqsk_alloc(const struct request_sock_ops *ops,
struct sock *sk_listener,
bool attach_listener)
{
// 创建request_sock 绑定listener和处理接口ops
struct request_sock *req = reqsk_alloc(ops, sk_listener,
attach_listener);
if (req) {
struct inet_request_sock *ireq = inet_rsk(req);
ireq->ireq_opt = NULL;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6)
ireq->pktopts = NULL;
#endif
atomic64_set(&ireq->ir_cookie, 0);
// 修改状态为TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV
ireq->ireq_state = TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV;
write_pnet(&ireq->ireq_net, sock_net(sk_listener));
ireq->ireq_family = sk_listener->sk_family;
}
return req;
}
通过源码可知 创建request_sock -> request_sock入队半连接队列 -> 发送SYN-ACK报文的顺序 。
并且创建的request_sock在创建出来后的状态为 TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV,这是个重要的细节。
2 · 接收ACK报文
根据 “初始化TCP Socket” 阶段的af_ops,其中的tcp_v4_syn_recv_sock定义了接受ACK后的处理逻辑。 而tcp_v4_syn_recv_sock中调用了 tcp_create_openreq_child,实现了 TCP_SYN_RECV的状态。
// net/ipv4/tcp_minisocks.c
struct sock *tcp_create_openreq_child(const struct sock *sk,
struct request_sock *req,
struct sk_buff *skb)
{
// 通过request_sock创建新的完整的sock
struct sock *newsk = inet_csk_clone_lock(sk, req, GFP_ATOMIC);
const struct inet_request_sock *ireq = inet_rsk(req);
struct tcp_request_sock *treq = tcp_rsk(req);
struct inet_connection_sock *newicsk;
const struct tcp_sock *oldtp;
struct tcp_sock *newtp;
u32 seq;
...
smc_check_reset_syn_req(oldtp, req, newtp);
/* Now setup tcp_sock */
...
if (sock_flag(newsk, SOCK_KEEPOPEN))
tcp_reset_keepalive_timer(newsk, keepalive_time_when(newtp));
newtp->rx_opt.tstamp_ok = ireq->tstamp_ok;
newtp->rx_opt.sack_ok = ireq->sack_ok;
newtp->window_clamp = req->rsk_window_clamp;
newtp->rcv_ssthresh = req->rsk_rcv_wnd;
newtp->rcv_wnd = req->rsk_rcv_wnd;
newtp->rx_opt.wscale_ok = ireq->wscale_ok;
// 省略大量对newtp的赋值,包括tcp握手确定的序列号,窗口大小等属性
...
newtp->bpf_chg_cc_inprogress = 0;
tcp_bpf_clone(sk, newsk);
__TCP_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), TCP_MIB_PASSIVEOPENS);
xa_init_flags(&newsk->sk_user_frags, XA_FLAGS_ALLOC1);
return newsk;
}
// net/ipv4/incet_connection_sock.c
struct sock *inet_csk_clone_lock(const struct sock *sk,
const struct request_sock *req,
const gfp_t priority)
{
struct sock *newsk = sk_clone_lock(sk, priority);
struct inet_connection_sock *newicsk;
struct inet_request_sock *ireq;
struct inet_sock *newinet;
if (!newsk)
return NULL;
newicsk = inet_csk(newsk);
newinet = inet_sk(newsk);
ireq = inet_rsk(req);
newicsk->icsk_bind_hash = NULL;
...
// 省略大量newicsk的赋值逻辑
...
/* Deinitialize accept_queue to trap illegal accesses. */
memset(&newicsk->icsk_accept_queue, 0,
sizeof(newicsk->icsk_accept_queue));
// 设置状态
inet_sk_set_state(newsk, TCP_SYN_RECV);
inet_clone_ulp(req, newsk, priority);
security_inet_csk_clone(newsk, req);
return newsk;
}
可以发现,通过request_sock创建的sock的状态被设置为了TCP_SYN_RECV。 说明TCP_SYN_RECV并不是第一次接受SYN报文后的状态,也不是request_sock的状态,而是三次握手后完整的sock的状态。
3 · 处理ACK报文
实际上会发现,上述的所有函数都是通过初始化的TCP Socket的af_ops执行,而af_ops则是通过Socket的tcp_rcv_state_process方法进行调用。
tcp_rcv_state_process方法是tcp_v4_rcv下的状态机流转逻辑,其中通过switch(sk->sk.state)定义了不同状态下的Socket接受TCP请求后状态流转的逻辑。
tcp_v4_syn_recv_sock统辖 创建sock , 放入全连接队列, 流转状态这几个步骤,确保他们的时序性。
// net/ipv4/tcp_input.c
enum skb_drop_reason
tcp_rcv_state_process(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
const struct tcphdr *th = tcp_hdr(skb);
struct request_sock *req;
int queued = 0;
SKB_DR(reason);
switch (sk->sk_state) {
case TCP_CLOSE:
SKB_DR_SET(reason, TCP_CLOSE);
goto discard;
// 接受第一个SYN报文的处理
case TCP_LISTEN:
if (th->ack)
return SKB_DROP_REASON_TCP_FLAGS;
if (th->rst) {
SKB_DR_SET(reason, TCP_RESET);
goto discard;
}
if (th->syn) {
if (th->fin) {
SKB_DR_SET(reason, TCP_FLAGS);
goto discard;
}
/* It is possible that we process SYN packets from backlog,
* so we need to make sure to disable BH and RCU right there.
*/
rcu_read_lock();
local_bh_disable();
// 通过af_ops调用conn_request逻辑
icsk->icsk_af_ops->conn_request(sk, skb);
local_bh_enable();
rcu_read_unlock();
consume_skb(skb);
return 0;
}
SKB_DR_SET(reason, TCP_FLAGS);
goto discard;
case TCP_SYN_SENT:
...
}
...
/* step 5: check the ACK field */
reason = tcp_ack(sk, skb, FLAG_SLOWPATH |
FLAG_UPDATE_TS_RECENT |
FLAG_NO_CHALLENGE_ACK);
...
//省略了RST重试请求的部分和等待发送方重新发送请求的部分
...
// 检查是否有af_ops处理接口 ipv4_specified
SKB_DR_SET(reason, NOT_SPECIFIED);
switch (sk->sk_state) {
case TCP_SYN_RECV:
tp->delivered++;
if (!tp->srtt_us)
tcp_synack_rtt_meas(sk, req);
if (tp->rx_opt.tstamp_ok)
tp->advmss -= TCPOLEN_TSTAMP_ALIGNED;
if (req) {
tcp_rcv_synrecv_state_fastopen(sk);
} else {
tcp_try_undo_spurious_syn(sk);
tp->retrans_stamp = 0;
tcp_init_transfer(sk, BPF_SOCK_OPS_PASSIVE_ESTABLISHED_CB,
skb);
WRITE_ONCE(tp->copied_seq, tp->rcv_nxt);
}
tcp_ao_established(sk);
smp_mb();
// TCP_SYN_RECV -> TCP_ESTABLISHED
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_ESTABLISHED);
sk->sk_state_change(sk);
...
/* Prevent spurious tcp_cwnd_restart() on first data packet */
tp->lsndtime = tcp_jiffies32;
tcp_initialize_rcv_mss(sk);
if (tcp_ecn_mode_accecn(tp))
tcp_accecn_third_ack(sk, skb, tp->syn_ect_snt);
tcp_fast_path_on(tp);
if (sk->sk_shutdown & SEND_SHUTDOWN)
tcp_shutdown(sk, SEND_SHUTDOWN);
break;
...
/* step 6: check the URG bit */
tcp_urg(sk, skb, th);
// 挥手逻辑
/* step 7: process the segment text */
switch (sk->sk_state) {
case TCP_CLOSE_WAIT:
case TCP_CLOSING:
case TCP_LAST_ACK:
...
case TCP_FIN_WAIT1:
case TCP_FIN_WAIT2:
...
}
客户端
1 · 发送SYN报文
通过调用tcp_v4_connect确定请求的四元组信息,其内部的tcp_connect则执行具体的tcp层的校验和发送逻辑。需要注意的是,TCP_CLOSE -> TCP_SYN_SENT的状态流转发生在SYN包发送前。
int tcp_v4_connect(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr_unsized *uaddr, int addr_len)
{
struct sockaddr_in *usin = (struct sockaddr_in *)uaddr;
struct inet_timewait_death_row *tcp_death_row;
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct ip_options_rcu *inet_opt;
struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
...
// 检查路由,找出去往目的IP的网卡网关
rt = ip_route_connect(fl4, nexthop, inet->inet_saddr,
sk->sk_bound_dev_if, IPPROTO_TCP, orig_sport,
orig_dport, sk);
if (IS_ERR(rt)) {
err = PTR_ERR(rt);
if (err == -ENETUNREACH)
IP_INC_STATS(net, IPSTATS_MIB_OUTNOROUTES);
return err;
}
...
// 省略了确定目标IP的部分
inet->inet_dport = usin->sin_port;
sk_daddr_set(sk, daddr);
inet_csk(sk)->icsk_ext_hdr_len = psp_sk_overhead(sk);
if (inet_opt)
inet_csk(sk)->icsk_ext_hdr_len += inet_opt->opt.optlen;
tp->rx_opt.mss_clamp = TCP_MSS_DEFAULT;
/* Socket identity is still unknown (sport may be zero).
* However we set state to SYN-SENT and not releasing socket
* lock select source port, enter ourselves into the hash tables and
* complete initialization after this.
*/
// 修改Socket状态
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_SYN_SENT);
// 确定源端口 若未bind,则内核分配一个临时端口
err = inet_hash_connect(tcp_death_row, sk);
if (err)
goto failure;
sk_set_txhash(sk);
// 使用新端口重新路由
rt = ip_route_newports(fl4, rt, orig_sport, orig_dport,
inet->inet_sport, inet->inet_dport, sk);
tp->tcp_usec_ts = dst_tcp_usec_ts(&rt->dst);
/* OK, now commit destination to socket. */
sk->sk_gso_type = SKB_GSO_TCPV4;
sk_setup_caps(sk, &rt->dst);
rt = NULL;
...
atomic_set(&inet->inet_id, get_random_u16());
if (tcp_fastopen_defer_connect(sk, &err))
return err;
if (err)
goto failure;
// 构建并发送SYN包
err = tcp_connect(sk);
if (err)
goto failure;
return 0;
failure:
...
}
// net/ipv4/tcp_output.c
int tcp_connect(struct sock *sk)
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct sk_buff *buff;
int err;
tcp_call_bpf(sk, BPF_SOCK_OPS_TCP_CONNECT_CB, 0, NULL);
...
// 省略了对目标IP的校验代码
...
// AO校验密钥不安全情况下的终止代码
if (inet_csk(sk)->icsk_af_ops->rebuild_header(sk))
return -EHOSTUNREACH; /* Routing failure or similar. */
// 初始化发送Socket
tcp_connect_init(sk);
if (unlikely(tp->repair)) {
tcp_finish_connect(sk, NULL);
return 0;
}
buff = tcp_stream_alloc_skb(sk, sk->sk_allocation, true);
if (unlikely(!buff))
return -ENOBUFS;
/* SYN eats a sequence byte, write_seq updated by
* tcp_connect_queue_skb().
*/
tcp_init_nondata_skb(buff, sk, tp->write_seq, TCPHDR_SYN);
...
/* Send off SYN; include data in Fast Open. */
// 发送SYN包给IP层
err = tp->fastopen_req ? tcp_send_syn_data(sk, buff) :
tcp_transmit_skb(sk, buff, 1, sk->sk_allocation);
if (err == -ECONNREFUSED)
return err;
/* We change tp->snd_nxt after the tcp_transmit_skb() call
* in order to make this packet get counted in tcpOutSegs.
*/
WRITE_ONCE(tp->snd_nxt, tp->write_seq);
tp->pushed_seq = tp->write_seq;
buff = tcp_send_head(sk);
if (unlikely(buff)) {
WRITE_ONCE(tp->snd_nxt, TCP_SKB_CB(buff)->seq);
tp->pushed_seq = TCP_SKB_CB(buff)->seq;
}
TCP_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), TCP_MIB_ACTIVEOPENS);
// 启动Timer计时器
/* Timer for repeating the SYN until an answer. */
tcp_reset_xmit_timer(sk, ICSK_TIME_RETRANS,
inet_csk(sk)->icsk_rto, false);
return 0;
}
2 · 接收SYN-ACK报文
接受方的调用逻辑跟服务端“接收SYN-ACK报文”的过程较为相似。调用链为:tcp_rcv_state_process -> tcp_rcv_synsent_state_process -> tcp_finish_connect并在最后的tcp_finish_connect中实现了状态的流转 TCP_SYN_SENT -> TCP_ESTABLISHED
// net/ipv4/tcp_input.c
enum skb_drop_reason
tcp_rcv_state_process(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
...
case TCP_SYN_SENT:
tp->rx_opt.saw_tstamp = 0;
tcp_mstamp_refresh(tp);
// 状态流转: TCP_SYN_SENT -> TCP
queued = tcp_rcv_synsent_state_process(sk, skb, th);
if (queued >= 0)
return queued;
/* Do step6 onward by hand. */
tcp_urg(sk, skb, th);
__kfree_skb(skb);
tcp_data_snd_check(sk);
return 0;
...
}
// net/ipv4/tcp_input.c
static int tcp_rcv_synsent_state_process(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct tcphdr *th)
{
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct tcp_fastopen_cookie foc = { .len = -1 };
int saved_clamp = tp->rx_opt.mss_clamp;
bool fastopen_fail;
SKB_DR(reason);
tcp_parse_options(sock_net(sk), skb, &tp->rx_opt, 0, &foc);
if (tp->rx_opt.saw_tstamp && tp->rx_opt.rcv_tsecr)
tp->rx_opt.rcv_tsecr -= tp->tsoffset;
if (th->ack) {
...
// 省略校验ACK序列号和时间戳的部分
...
// 省略了rst报文的重置连接部分
WRITE_ONCE(tp->rcv_nxt, TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq + 1);
tp->rcv_wup = TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq + 1;
/* RFC1323: The window in SYN & SYN/ACK segments is
* never scaled.
*/
tp->snd_wnd = ntohs(th->window);
...
// 省略了tcp请求头的校验
tcp_sync_mss(sk, icsk->icsk_pmtu_cookie);
tcp_initialize_rcv_mss(sk);
/* Remember, tcp_poll() does not lock socket!
* Change state from SYN-SENT only after copied_seq
* is initialized. */
WRITE_ONCE(tp->copied_seq, tp->rcv_nxt);
smc_check_reset_syn(tp);
smp_mb();
// 连接完成的状态流转
tcp_finish_connect(sk, skb);
fastopen_fail = (tp->syn_fastopen || tp->syn_data) &&
tcp_rcv_fastopen_synack(sk, skb, &foc);
...
}
/* No ACK in the segment */
if (th->rst) {
...
}
...
if (th->syn) {
// 这里体现了"双向连接"的处理逻辑
// 即客户端等待服务端回复SYN-ACK的过程中,得到了仅有SYN的报文
...
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_SYN_RECV);
...
tcp_send_synack(sk);
#if 0
return -1;
#else
goto consume;
#endif
}
// net/ipv4/tcp_input.c
void tcp_finish_connect(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
// 连接简历完成处理
tcp_ao_finish_connect(sk, skb);
// 状态机流转 TCP_SYN_SENT -> TCP_ESTABLISHED
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_ESTABLISHED);
icsk->icsk_ack.lrcvtime = tcp_jiffies32;
if (skb) {
icsk->icsk_af_ops->sk_rx_dst_set(sk, skb);
security_inet_conn_established(sk, skb);
sk_mark_napi_id(sk, skb);
}
tcp_init_transfer(sk, BPF_SOCK_OPS_ACTIVE_ESTABLISHED_CB, skb);
...
}
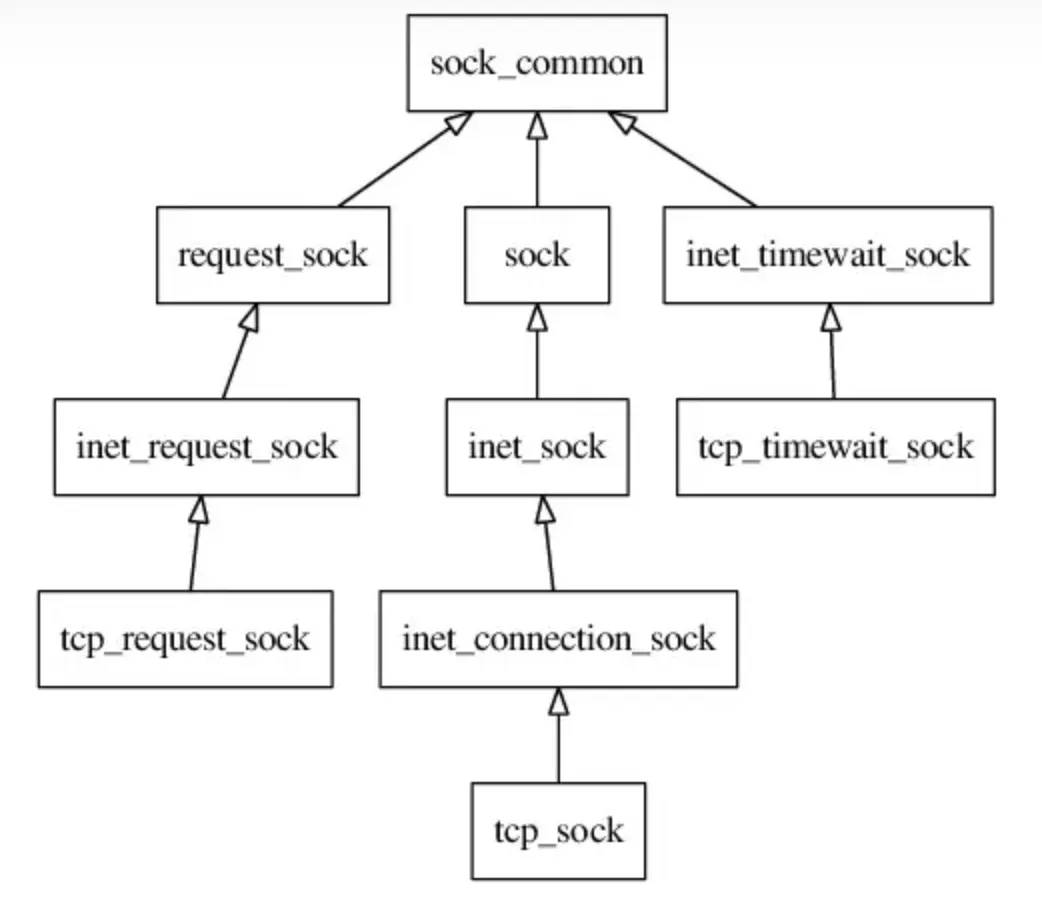
sock的类型
下述几种sock类型,可以当作是父类-子类关系,C语言中结构体里的内存是连续的,将要继承的”父类”,放到结构体的第一位,然后就可以通过强制转换进行继承访问。
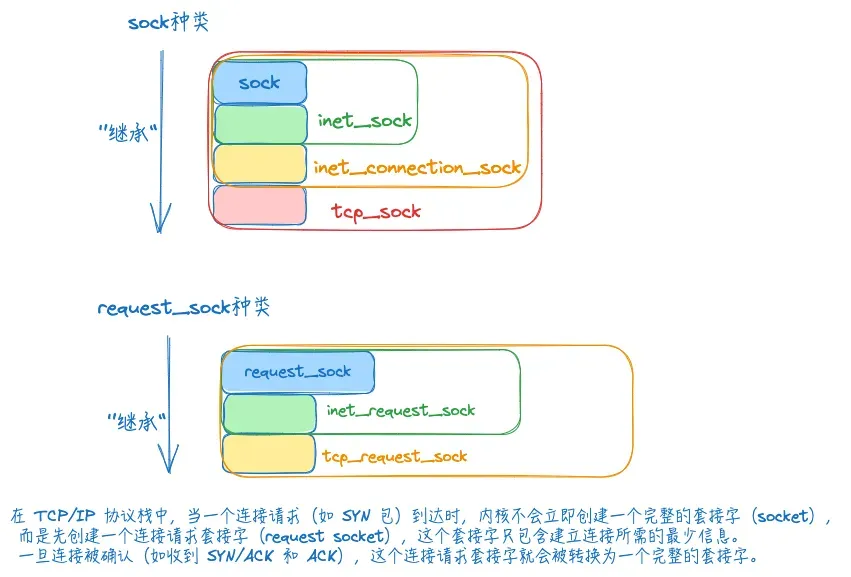
sock
所有sock类的基底,基础的数据结构,用于维护任何协议都使用到的数据收发缓冲区。
// include\net\sock.h
struct sock {
struct sock_common __sk_common;
socket_lock_t sk_lock;
atomic_t sk_drops;
int sk_rcvlowat;
struct sk_buff_head sk_error_queue;
struct sk_buff *sk_rx_skb_cache;
struct sk_buff_head sk_receive_queue;
...
struct proto *skc_prot;
...
}
常说的socket()系统调用,本质就是创建了一个struct sock的结构体。同时由于Linux一切皆文件的设计理念,还需要对struct sock和struct file进行一个映射操作。__sys_socket -> sock_create -> __sock_create -> pf->create -> inet_create其中涉及了RCU(Read-Copy Update) 的理念,用于适应socket高频读取低频写入的场景。 这里”Copy”其实就是指读写隔离的实现方式。写操作不会原地修改,而是copy一份新的数据后进行修改(保证原子性)。而读操作会读取旧数据。并且他的删除是延迟释放,socket的内存不会在close()后立刻释放,而是后台静默延迟处理。
inet_sock
特指用了网络传输功能的sock,在sock的基础上还加入了TTL,端口,IP地址这些跟网络传输相关的字段信息。
struct inet_sock {
/* sk and pinet6 has to be the first two members of inet_sock */
struct sock sk;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IPV6)
struct ipv6_pinfo *pinet6;
struct ipv6_fl_socklist __rcu *ipv6_fl_list;
#endif
/* Socket demultiplex comparisons on incoming packets. */
#define inet_daddr sk.__sk_common.skc_daddr
#define inet_rcv_saddr sk.__sk_common.skc_rcv_saddr
#define inet_dport sk.__sk_common.skc_dport
#define inet_num sk.__sk_common.skc_num
unsigned long inet_flags;
__be32 inet_saddr;
__s16 uc_ttl;
__be16 inet_sport;
struct ip_options_rcu __rcu *inet_opt;
atomic_t inet_id;
__u8 min_ttl;
__u8 mc_ttl;
...
struct ip_mc_socklist __rcu *mc_list;
struct inet_cork_full cork;
};
inet_connection_sock
在inet_sock的基础上面向连接的sock结构体,增加了连接相关的字段属性,比如accept队列,握手失败重试次数,数据包分片大小等信息。源码中经常看到的 icsk 前缀其实就是指inet_connection_sock
// include/net/inet_connection_sock.h
struct inet_connection_sock {
/* inet_sock has to be the first member! */
struct inet_sock icsk_inet;
struct request_sock_queue icsk_accept_queue;
struct inet_bind_bucket *icsk_bind_hash;
struct inet_bind2_bucket *icsk_bind2_hash;
struct timer_list icsk_delack_timer;
union {
struct timer_list icsk_keepalive_timer;
struct timer_list mptcp_tout_timer;
};
__u32 icsk_rto;
__u32 icsk_rto_min;
u32 icsk_rto_max;
__u32 icsk_delack_max;
__u32 icsk_pmtu_cookie;
const struct tcp_congestion_ops *icsk_ca_ops;
const struct inet_connection_sock_af_ops *icsk_af_ops;
const struct tcp_ulp_ops *icsk_ulp_ops;
void __rcu *icsk_ulp_data;
...
};
tcp_sock
tcp_sock就是tcp协议专用的sock结构,在inet_connection_sock基础上还加入了tcp特有的滑动窗口、拥塞避免等功能。
// include/linux/tcp.h
struct tcp_sock {
/* inet_connection_sock has to be the first member of tcp_sock */
struct inet_connection_sock inet_conn;
u16 tcp_header_len; /* Bytes of tcp header to send */
u16 gso_segs; /* Max number of segs per GSO packet */
...
u32 snd_wnd; /* The window we expect to receive */
u32 max_window; /* Maximal window ever seen from peer */
...
u32 snd_cwnd; /* Sending congestion window */
u32 snd_cwnd_cnt; /* Linear increase counter */
...
}
半连接队列何去何从?
在inet_listen()中,只有对全连接队列和FastOpen队列的初始化,没有半连接队列的相关处理。同时sock类中也只有全连接链表的头和尾,没有半连接队列的操作符。这是因为独立的半连接队列已经不存在了,转变为了一种概念。 服务端接收SYN报文后创建的request_sock插入到全局连接表ehash中进行管理,监听sock中只保留young和qlen参数进行半连接队列容量的监控。tcp_conn_request() -> inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add() -> reqsk_queue_hash_req>reqsk_queue_hash_req-> inet_ehash_insert
// net/ipv4/tcp_input.c/tcp_conn_request()
if (fastopen_sk) {
// FastOpen连接,一次SYN直接入全连接队列完成握手
af_ops->send_synack(fastopen_sk, dst, &fl, req,
&foc, TCP_SYNACK_FASTOPEN, skb);
/* Add the child socket directly into the accept queue */
if (!inet_csk_reqsk_queue_add(sk, req, fastopen_sk)) {
bh_unlock_sock(fastopen_sk);
sock_put(fastopen_sk);
goto drop_and_free;
}
sk->sk_data_ready(sk);
bh_unlock_sock(fastopen_sk);
sock_put(fastopen_sk);
} else {
// 入半连接队列后发送SYN-ACK报文
tcp_rsk(req)->tfo_listener = false;
if (!want_cookie &&
unlikely(!inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add(sk, req))) {
reqsk_free(req);
dst_release(dst);
return 0;
}
// 通过操作符发送SYN-ACK报文
af_ops->send_synack(sk, dst, &fl, req, &foc,
!want_cookie ? TCP_SYNACK_NORMAL :
TCP_SYNACK_COOKIE,
skb);
if (want_cookie) {
reqsk_free(req);
return 0;
}
}
// net/ipv4/inet_connection_sock.c
bool inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add(struct sock *sk, struct request_sock *req)
{
// 递进
if (!reqsk_queue_hash_req(req))
returnfalse;
inet_csk_reqsk_queue_added(sk);
returntrue;
}
// net/ipv4/inect_connection_sock.c
static bool reqsk_queue_hash_req(struct request_sock *req)
{
bool found_dup_sk = false;
// 插入全局ehash表
if (!inet_ehash_insert(req_to_sk(req), NULL, &found_dup_sk))
returnfalse;
/* The timer needs to be setup after a successful insertion. */
req->timeout = tcp_timeout_init((struct sock *)req);
timer_setup(&req->rsk_timer, reqsk_timer_handler, TIMER_PINNED);
mod_timer(&req->rsk_timer, jiffies + req->timeout);
/* before letting lookups find us, make sure all req fields
* are committed to memory and refcnt initialized.
*/
smp_wmb();
refcount_set(&req->rsk_refcnt, 2 + 1);
returntrue;
}
listen socket 的 struct sock 数据结构 inet_connection_sock。
● 全连接队列和半连接队列最大长度: inet_connection_sock.icsk_inet.sock.sk_max_ack_backlog
● 全连接队列: inet_connection_sock.icsk_accept_queue.rskq_accept_head
● 当前全连接队列长度: inet_connection_sock.icsk_inet.sock.sk_ack_backlog
● 半连接队列(哈希表): inet_hashinfo.inet_ehash_bucket
● 当前半连接队列长度: inet_connection_sock.icsk_accept_queue.qlen
拓展思考
源码如何体现request_sock向sock的转变?
不存在直接的转变,而是创建一个sock挂载到原来的request_sock下。
全连接队列的sk_ack_backlog和sk_max_ack_backlog分别是什么意思?
sk_ack_backlog是当前全连接队列中的元素数量,sk_max_ack_backlog是全连接队列和半连接队列的最大长度。
什么是FastOpen?FastOpen队列有什么用?
用于进行SYN Cookie模式下的交互。这是Google提出的一种通信机制,在原本不携带数据信息的SYN请求中携带信息,进行快速的握手和通信。
 夜雨聆风
夜雨聆风





