Vue v2.6.11 生命周期源码解析
注:建议学习源码从易到难(学习react也可建议先学习react16),核心是感受框架设计的理念,学习vue2后,再去对照学习vue3,从中对比效果更好。
github源码地址:
https://github.com/vuejs/vue/tree/v2.6.11
源码学习路线(红色是重点了解模块)
-
响应式实现篇
学习Vue中如何实现数据的响应式系统,从而达到数据驱动视图
-
虚拟 DOM 篇
学习什么是虚拟 DOM,以及Vue中的DOM-Diff原理
-
模板编译篇
学习Vue内部是怎么把template模板编译成虚拟DOM,从而渲染出真实DOM
-
实例方法篇
学习Vue中所有实例方法(即所有以$开头的方法)的实现原理
-
全局 API 篇
学习Vue中所有全局API的实现原理
-
生命周期篇
学习Vue中组件的生命周期实现原理
-
指令篇
学习Vue中所有指令的实现原理
-
过滤器篇
学习Vue中所有过滤器的实现原理
-
内置组件篇
学习Vue中内置组件的实现原理
项目目录:complier 和 core 是核心
├─dist # 项目构建后的文件├─scripts # 与项目构建相关的脚本和配置文件├─flow # flow的类型声明文件├─src # 项目源代码│ ├─complier # 与模板编译相关的代码│ ├─core # 通用的、与运行平台无关的运行时代码│ │ ├─observe # 实现变化侦测的代码│ │ ├─vdom # 实现virtual dom的代码│ │ ├─instance # Vue.js实例的构造函数和原型方法│ │ ├─global-api # 全局api的代码│ │ └─components # 内置组件的代码│ ├─server # 与服务端渲染相关的代码│ ├─platforms # 特定运行平台的代码,如weex│ ├─sfc # 单文件组件的解析代码│ └─shared # 项目公用的工具代码└─test # 项目测试代码
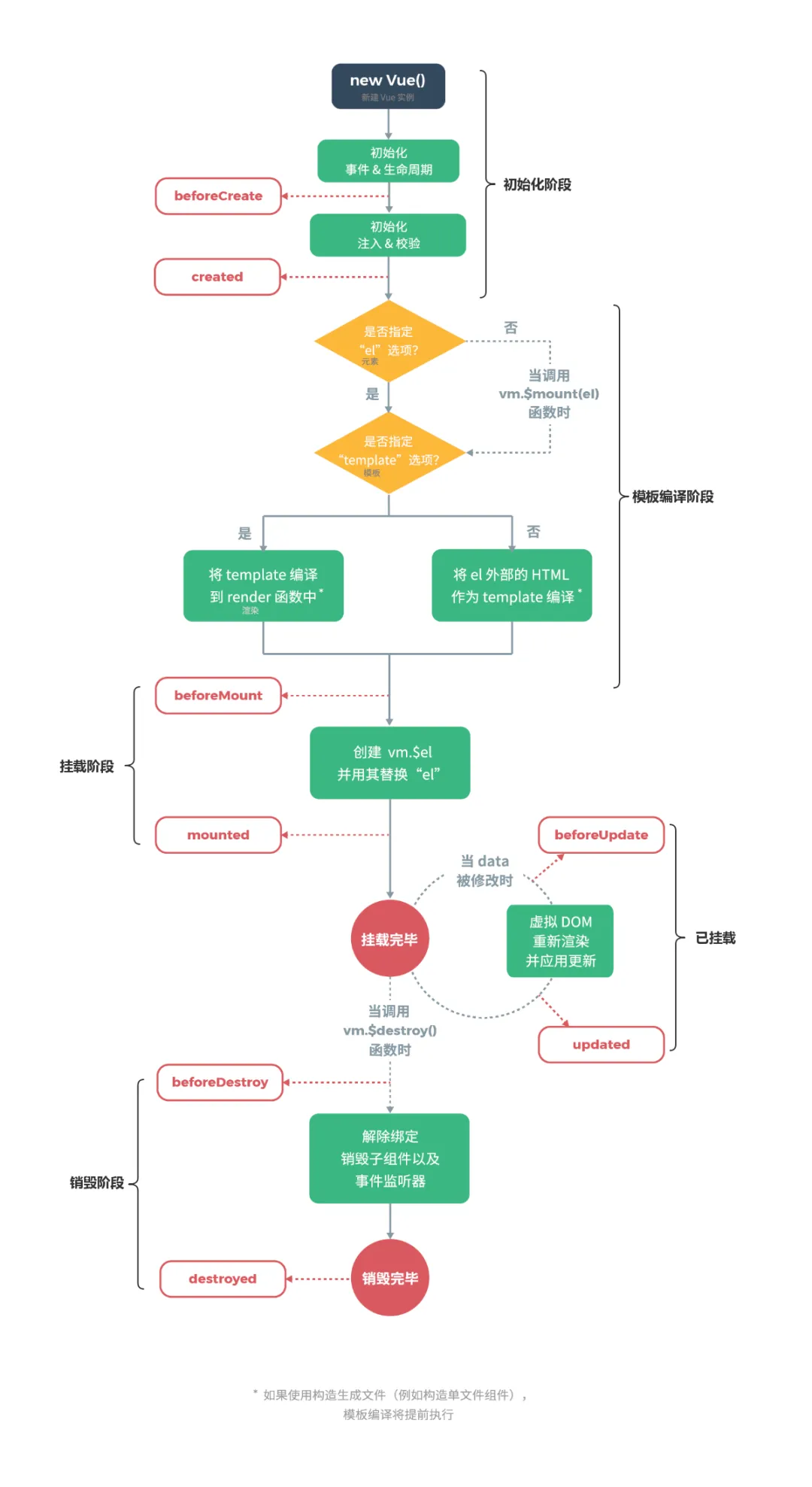
从图中我们可以看到,Vue实例的生命周期大致可分为4个阶段:
-
初始化阶段:为
Vue实例上初始化一些属性,事件以及响应式数据; -
模板编译阶段:将模板编译成渲染函数;
-
挂载阶段:将实例挂载到指定的
DOM上,即将模板渲染到真实DOM中; -
销毁阶段:将实例自身从父组件中删除,并取消依赖追踪及事件监听器;
new Vue()
源码位置:src/core/instance/index.js
function Vue (options) {if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !(this instanceof Vue)) {warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the new keyword')}this._init(options)}
export function initMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {const vm: Component = this// a uidvm._uid = uid++let startTag, endTag/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {startTag = vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}endTag = vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}mark(startTag)}// a flag to avoid this being observedvm._isVue = true// merge optionsif (options && options._isComponent) {// optimize internal component instantiation// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the// internal component options needs special treatment.initInternalComponent(vm, options)} else {vm.$options = mergeOptions(// 简单理解为返回vm.constructor.options.相当于Vue.optionsresolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),options || {},vm)}/* istanbul ignore else */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {initProxy(vm)} else {vm._renderProxy = vm}// expose real selfvm._self = vminitLifecycle(vm)initEvents(vm)initRender(vm)callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/propsinitState(vm)initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/propscallHook(vm, 'created')/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false)mark(endTag)measure(vue ${vm._name} init, startTag, endTag)}if (vm.$options.el) {vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)}}}export function initGlobalAPI (Vue: GlobalAPI) {// configconst configDef = {}configDef.get = () => configif (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {configDef.set = () => {warn('Do not replace the Vue.config object, set individual fields instead.')}}Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'config', configDef)// exposed util methods.// NOTE: these are not considered part of the public API - avoid relying on// them unless you are aware of the risk.Vue.util = {warn,extend,mergeOptions,defineReactive}Vue.set = setVue.delete = delVue.nextTick = nextTick// 2.6 explicit observable APIVue.observable = <T>(obj: T): T => {observe(obj)return obj}// 创建了一个空的optionsVue.options = Object.create(null)ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {Vue.options[type + 's'] = Object.create(null)})/*Vue.options.components = {};Vue.options.directives = {};Vue.options.filter = {};*/// this is used to identify the "base" constructor to extend all plain-object// components with in Weex's multi-instance scenarios.Vue.options._base = Vueextend(Vue.options.components, builtInComponents)initUse(Vue)initMixin(Vue)initExtend(Vue)initAssetRegisters(Vue)}export const ASSET_TYPES = ['component','directive','filter']function mergeHook (parentVal: ?Array<Function>,childVal: ?Function | ?Array<Function>): ?Array<Function> {const res = childVal? parentVal? parentVal.concat(childVal): Array.isArray(childVal)? childVal: [childVal]: parentValreturn res? dedupeHooks(res): res}function mergeHook(parentVal, childVal) {if (childVal) {if (parentVal) {return parentVal.concat(childVal)} else {if (Array.isArray(childVal)) {return childVal} else {return [childVal]}} else {return parentVal}}}export function callHook (vm: Component, hook: string) {// #7573 disable dep collection when invoking lifecycle hookspushTarget()const handlers = vm.$options[hook]const info = `${hook} hook`if (handlers) {for (let i = 0, j = handlers.length; i < j; i++) {invokeWithErrorHandling(handlers[i], vm, null, vm, info)}}if (vm._hasHookEvent) {vm.$emit('hook:' + hook)}popTarget()}
initLifecycle
export function initLifecycle (vm: Component) {const options = vm.$options// locate first non-abstract parentlet parent = options.parentif(parent && !options.abstract) {while(parent.$options.abstract && parent.$parent) {parent = parent.$parent}parent.$children.push(vm)}vm.$parent = parentvm.$root = parent ? parent.$root : vmvm.$children = []vm.$refs = {}vm._watcher = nullvm._inactive = nullvm._directInactive = falsevm._isMounted = falsevm._isDestroyed = falsevm._isBeingDestroyed = false}
initEvents
<child @select="selectHandler" @click.native="clickHandler"></child>el.events = {select: {value: 'selectHandler'}}el.nativeEvents = {click: {value: "clickHandler"}}// event handlersif (el.events) {data += ${genHandlers(el.events, false)},}if (el.nativeEvents) {data += ${genHandlers(el.nativeEvents, true)},}{on: {"select": selectHandlder},nativeOn: {"click": function($event) {return clickHandler($event)}}}// extract listeners, since these needs to be treated as// child component listeners instead of DOM listenersconst listeners = data.on// replace with listeners with .native modifier// so it gets processed during parent component patch.data.on = data.nativeOn
结论: 父组件给子组件的注册事件中,把自定义事件传给子组件,在子组件实例化的时候进行初始化,而浏览器原生事件是在父组件中处理的。
也就是说,实例初始化阶段调用initEvents实际上初始化的是父组件在模版中使用v-on或@注册的监听子组件内触发的事件。
export function initEvents (vm: Component) {vm._events = Object.create(null)vm._hasHookEvent = false// init parent attached eventsconst listeners = vm.$options._parentListenersif (listeners) {updateComponentListeners(vm, listeners)}}
initInjections
允许一个祖先组件向子孙后代组件注入一个依赖,不论组件层级有多深,都始终生效。
inject选项可以是一个字符串数组或一个对象。
// 父组件var parent = {provide: {foo: 'bar'}}var child = {inject: ['foo'],create() {console.log(this.foo) // "bar"}}
const s = Symbol()const Provider = {provide() {return {[s]: 'foo'}}}const child = {inject: { s }}
provide 和 inject 选项绑定的数据不是响应式的。
const child = {inject: ['foo'],data() {return {bar: this.foo}}}
源码位置:src/core/instance/inject.js
export function initProvide (vm: Component) {const provide = vm.$options.provideif (provide) {vm._provided = typeof provide === 'function'? provide.call(vm): provide}}export function initInjections (vm: Component) {const result = resolveInject(vm.$options.inject, vm)if (result) {toggleObserving(false)Object.keys(result).forEach(key => {/* istanbul ignore else */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {defineReactive(vm, key, result[key], () => {warn(`Avoid mutating an injected value directly since the changes will be ` +`overwritten whenever the provided component re-renders. ` +`injection being mutated: "${key}"`,vm)})} else {defineReactive(vm, key, result[key])}})toggleObserving(true)}}
export function resolveInject (inject: any, vm: Component): ?Object {if (inject) {// inject is :any because flow is not smart enough to figure out cachedconst result = Object.create(null)const keys = hasSymbol? Reflect.ownKeys(inject): Object.keys(inject)for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {const key = keys[i]// #6574 in case the inject object is observed...if (key === '__ob__') continueconst provideKey = inject[key].fromlet source = vmwhile (source) {if (source._provided && hasOwn(source._provided, provideKey)) {result[key] = source._provided[provideKey]break}source = source.$parent}if (!source) {if ('default' in inject[key]) {const provideDefault = inject[key].defaultresult[key] = typeof provideDefault === 'function'? provideDefault.call(vm): provideDefault} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {warn(`Injection "${key}" not found`, vm)}}}return result}}
对于字符串数组,在_init中调用合并属性的时候去处理,通过normalizeInject。
源码位置:src/core/util/options.js
function normalizeInject (options: Object, vm: ?Component) {const inject = options.injectif (!inject) returnconst normalized = options.inject = {}if (Array.isArray(inject)) {for (let i = 0; i < inject.length; i++) {normalized[inject[i]] = { from: inject[i] }}} else if (isPlainObject(inject)) {for (const key in inject) {const val = inject[key]normalized[key] = isPlainObject(val)? extend({ from: key }, val): { from: val }}} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {warn(Invalid value for option "inject" : expected an Array or an Object, + but got ${toRawType(inject)}.,vm)}}
initState
源码位置:src/core/instance/state.js
export function initState (vm: Component) {vm._watchers = []const opts = vm.$optionsif (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)if (opts.data) {initData(vm)} else {observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)}if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {initWatch(vm, opts.watch)}}
props: ['name']props: {name: String}props: {name: {type: String}}
normalizeProps
源码位置:src/core/util/options.js
function normalizeProps (options: Object, vm: ?Component) {const props = options.propsif (!props) returnconst res = {}let i, val, nameif (Array.isArray(props)) {i = props.lengthwhile (i--) {val = props[i]if (typeof val === 'string') {name = camelize(val)res[name] = { type: null }} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {warn('props must be strings when using array syntax.')}}} else if (isPlainObject(props)) {for (const key in props) {val = props[key]name = camelize(key)res[name] = isPlainObject(val)? val: { type: val }}} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {warn(Invalid value for option "props": expected an Array or an Object, + but got ${toRawType (props)}.,vm)}options.props = res}
将props数据规范化处理后,交给 initProps处理。
源码位置:src/core/instance/state.js
functioninitProps (vm: Component, propsOptions: Object) {const propsData = vm.$options.propsData || {}const props = vm._props = {}// cache prop keys so that future props updates can iterate using Array// instead of dynamic object key enumeration.// 用来缓存props对象中的key,将来更新props时只需要遍历m.$options._propKeys数组即可得到所有props的keyconst keys = vm.$options._propKeys = []const isRoot = !vm.$parent// root instance props should be convertedif(!isRoot) {toggleObserving(false)}for(const key in propsOptions) {keys.push(key)const value = validateProp(key, propsOptions, propsData, vm)/* istanbul ignore else */if(process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {const hyphenatedKey = hyphenate(key)if(isReservedAttribute(hyphenatedKey) ||config.isReservedAttr(hyphenatedKey)) {warn("${hyphenatedKey}" is a reserved attribute and cannot be used as component prop.,vm)}defineReactive(props, key, value, () => {if(!isRoot && !isUpdatingChildComponent) {warn(Avoid mutating a prop directly since the value will be + overwritten whenever the parent component re-renders. + Instead, use a data or computed property based on the prop's +value. Prop being mutated: "${key}",vm)}})} else {defineReactive(props, key, value)}// static props are already proxied on the component's prototype// during Vue.extend(). We only need to proxy props defined at// instantiation here.if(!(key in vm)) {proxy(vm, _props, key)}}toggleObserving(true)}export function validateProp (key: string,propOptions: Object,propsData: Object,vm?: Component): any {const prop = propOptions[key]const absent = !hasOwn(propsData, key)let value = propsData[key]// boolean castingconst booleanIndex = getTypeIndex(Boolean, prop.type)if(booleanIndex > -1) {// 父组件没有传入该prop属性并且该属性也没有默认值if(absent && !hasOwn(prop, 'default')) {value = false} else if (value === '' || value === hyphenate(key)) {// only cast empty string / same name to boolean if// boolean has higher priorityconst stringIndex = getTypeIndex(String, prop.type)if(stringIndex < 0 || booleanIndex < stringIndex) {value = true}}}// check default valueif(value === undefined) {value = getPropDefaultValue(vm, prop, key)// since the default value is a fresh copy,// make sure to observe it.const prevShouldObserve = shouldObservetoggleObserving(true)observe(value)toggleObserving(prevShouldObserve)}if(process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&// skip validation for weex recycle-list child component props!(__WEEX__ && isObject(value) && ('@binding' in value))) {assertProp(prop, key, value, vm, absent)}return value}functiongetPropDefaultValue (vm: ?Component, prop: PropOptions, key: string): any{// no default, return undefinedif(!hasOwn(prop, 'default')) {return undefined}const def = prop.default// warn against non-factory defaults for Object & Arrayif(process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && isObject(def)) {warn('Invalid default value for prop "' + key + '": ' +'Props with type Object/Array must use a factory function ' +'to return the default value.',vm)}// the raw prop value was also undefined from previous render,// return previous default value to avoid unnecessary watcher triggerif(vm && vm.$options.propsData && vm.$options.propsData[key] === undefined &&vm._props[key] !== undefined) {return vm._props[key]}// call factory function for non-Function types// a value is Function if its prototype is function even across different execution contextreturn typeof def === 'function' && getType(prop.type) !== 'Function'? def.call(vm): def}
function assertProp (prop: PropOptions,name: string,value: any,vm: ?Component,// 判断当前key是否在propsData中存在,也就是父组件是否传入了该属性absent: boolean) {if (prop.required && absent) {warn('Missing required prop: "' + name + '"',vm)return}if (value == null && !prop.required) {return}let type = prop.type// props: {name: true}let valid = !type || type === trueconst expectedTypes = []if (type) {if (!Array.isArray(type)) {type = [type]}for (let i = 0; i < type.length && !valid; i++) {/*{valid: true // 表示校验是否成功expectedType: 'Boolean' | 'String'.. // 表示被校验的类型}*/const assertedType = assertType(value, type[i])expectedTypes.push(assertedType.expectedType || '')valid = assertedType.valid}}if (!valid) {warn(getInvalidTypeMessage(name, value, expectedTypes),vm)return}const validator = prop.validatorif (validator) {if (!validator(value)) {warn('Invalid prop: custom validator check failed for prop "' + name + '".',vm)}}}
initMethods
function initMethods (vm: Component, methods: Object) {const props = vm.$options.props;for (const key in methods) {if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {if (typeof methods[key] !== 'function') {warn(`Method "${key}" has type "${typeof methods[key]}" in the component definition. ` +`Did you reference the function correctly?`,vm)}if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {warn(`Method "${key}" has already been defined as a prop.`,vm)}// isReserved 判断函数是以_ 或 $ 开头的if ((key in vm) && isReserved(key)) {warn(`Method "${key}" conflicts with an existing Vue instance method. ` +`Avoid defining component methods that start with _ or $.`)}}vm[key] = typeof methods[key] !== 'function' ? noop : bind(methods[key], vm)}}
initData
function initData (vm: Component) {let data = vm.$options.datadata = vm._data = typeof data === 'function'? getData(data, vm): data || {}if (!isPlainObject(data)) {data = {}process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn('data functions should return an object:\n' +'https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#data-Must-Be-a-Function',vm)}// proxy data on instanceconst keys = Object.keys(data)const props = vm.$options.propsconst methods = vm.$options.methodslet i = keys.lengthwhile (i--) {const key = keys[i]if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {if (methods && hasOwn(methods, key)) {warn(`Method "${key}" has already been defined as a data property., vm) } } if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) { process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(The data property "${key}" is already declared as a prop. + Use prop default value instead., vm)} else if (!isReserved(key)) { // 通过proxy代理到vm上,我们就可以通过this.xxx来访问data的数据了 proxy(vm, _data`, key)}}// observe dataobserve(data, true /* asRootData */)}
initComputed
const vm = new Vue({data: {a: 1},computed: {adouble: function() {return this.data * 2},aPlus: {get: function() {return this.a + 1},set: function(v) {this.a = v - 1}}}})
function initComputed (vm: Component, computed: Object) {// $flow-disable-lineconst watchers = vm._computedWatchers = Object.create(null)// computed properties are just getters during SSRconst isSSR = isServerRendering()for (const key in computed) {const userDef = computed[key]const getter = typeof userDef === 'function' ? userDef : userDef.getif (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && getter == null) {warn(Getter is missing for computed property "${key}".,vm)}if (!isSSR) {// create internal watcher for the computed property.watchers[key] = new Watcher(vm,getter || noop,noop,computedWatcherOptions)}// component-defined computed properties are already defined on the// component prototype. We only need to define computed properties defined// at instantiation here.if (!(key in vm)) {defineComputed(vm, key, userDef)} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {if (key in vm.$data) {warn(`The computed property "${key}" is already defined in data., vm)} else if (vm.$options.props && key in vm.$options.props) {warn(The computed property "${key}" is already defined as a prop.`, vm)}}}}
// 给target定义一个属性key,并且属性key的getter和setter根据userDef的值来设置export function defineComputed (target: any,key: string,userDef: Object | Function) {const shouldCache = !isServerRendering()if (typeof userDef === 'function') {sharedPropertyDefinition.get = shouldCache// 需要创建一个具有缓存功能的getter? createComputedGetter(key)// 服务端环境下计算属性不需要缓存的: createGetterInvoker(userDef)sharedPropertyDefinition.set = noop} else {sharedPropertyDefinition.get = userDef.get? shouldCache && userDef.cache !== false? createComputedGetter(key): createGetterInvoker(userDef.get): noopsharedPropertyDefinition.set = userDef.set || noop}if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&sharedPropertyDefinition.set === noop) {sharedPropertyDefinition.set = function () {warn(Computed property "${key}"was assigned to but it has no setter.,this)}}Object.defineProperty(target, key, sharedPropertyDefinition)}function createComputedGetter (key) {return function computedGetter () {const watcher = this._computedWatchers && this._computedWatchers[key]if (watcher) {if (watcher.dirty) {watcher.evaluate()}if (Dep.target) {watcher.depend()}return watcher.value}}}depend () {let i = this.deps.lengthwhile (i--) {this.deps[i].depend()}}evaluate () {this.value = this.get()this.dirty = false}update () {/* istanbul ignore else */if (this.lazy) {this.dirty = true} else if (this.sync) {this.run()} else {queueWatcher(this)}}
new Watcher的时候,传入
{computed: true}
initWatch
const vm = new Vue({data: {a: 1,b: 2,c: 3},watch: {a: function(val, oldVal) {},b: 'someMethod',c: {handler: function(val, oldVal) {...},deep: true},d: {handler: 'xxx',immediate: true},e: ['handler',functionhander2 (val, oldVal) {...}]//"e.f": function (val, oldVal) {...}}})
function initWatch (vm: Component, watch: Object) {for (const key in watch) {const handler = watch[key]if (Array.isArray(handler)) {for (let i = 0; i < handler.length; i++) {createWatcher(vm, key, handler[i])}} else {createWatcher(vm, key, handler)}}}
function createWatcher (vm: Component,expOrFn: string | Function,handler: any,options?: Object) {if (isPlainObject(handler)) {options = handlerhandler = handler.handler}// 在initMehotds的时候已经将选项中的每一个方法都绑定到当前实例上了if (typeof handler === 'string') {handler = vm[handler]}return vm.$watch(expOrFn, handler, options)}
挂载阶段
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el?: string | Element,hydrating?: boolean): Component {el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefinedreturn mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)}
updateComponent = () => {const name = vm._nameconst id = vm._uidconst startTag = vue-perf-start:${id}const endTag = vue-perf-end:${id}mark(startTag)const vnode = vm._render()mark(endTag)measure(vue ${name} render, startTag, endTag)mark(startTag)vm._update(vnode, hydrating)mark(endTag)measure(vue ${name} patch, startTag, endTag)}// we set this to vm._watcher inside the watcher's constructor// since the watcher's initial patch may call $forceUpdate (e.g. inside child// component's mounted hook), which relies on vm._watcher being already defined// updateComponent中读取到的所有数据,都会被watcher所监控,这些数据中只要有一个发生变化,那么watcher就会得到通知,从而去更新视图new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {before () {if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')}}}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
销毁阶段
Vue.prototype.$destroy = function () {const vm: Component = this// 标志当前实例是否处于正在被销毁的阶段if(vm._isBeingDestroyed) {return}callHook(vm, 'beforeDestroy')vm._isBeingDestroyed = true// remove self from parentconst parent = vm.$parent// 把自己从父级实例的子实例列表中删除if(parent && !parent._isBeingDestroyed && !vm.$options.abstract) {remove(parent.$children, vm)}// 一部分是实例自身依赖其他数据,需要将实例自身从其他数据的依赖列表中删除// 另一部分是实例内的数据对其他数据的依赖,也需要从其他数据的依赖列表中删除实例内数据// teardown watchersif(vm._watcher) {// 从所有依赖向的Dep列表中将自己删除vm._watcher.teardown()}let i = vm._watchers.lengthwhile(i--) {vm._watchers[i].teardown()}// remove reference from data ob// frozen object may not have observer.if(vm._data.__ob__) {vm._data.__ob__.vmCount--}// call the last hook...vm._isDestroyed = true// invoke destroy hooks on current rendered treevm.__patch__(vm._vnode, null)// fire destroyed hookcallHook(vm, 'destroyed')// turn off all instance listeners.// 移除实例的所有事件监听器vm.$off()// remove __vue__ referenceif(vm.$el) {vm.$el.__vue__ = null}// release circular reference (#6759)if(vm.$vnode) {vm.$vnode.parent = null}}
 夜雨聆风
夜雨聆风





