Flink源码阅读:JobManager的HA机制
JobManager 在 Flink 集群中发挥着重要的作用,包括任务调度和资源管理等工作。如果 JobManager 宕机,那么整个集群的任务都将失败。为了解决 JobManager 的单点问题,Flink 也设计了 HA 机制来保障整个集群的稳定性。
基本概念
在 JobManager 启动时,调用 HighAvailabilityServicesUtils.createHighAvailabilityServices 来创建 HA 服务,HA 依赖的服务都被封装在 HighAvailabilityServices 中。当前 Flink 内部支持两种高可用模式,分别是 ZooKeeper 和 KUBERNETES。
case ZOOKEEPER:
return createZooKeeperHaServices(configuration, executor, fatalErrorHandler);
case KUBERNETES:
return createCustomHAServices(
"org.apache.flink.kubernetes.highavailability.KubernetesHaServicesFactory",
configuration,
executor);
HighAvailabilityServices 中提供的关键组件包括:
-
LeaderRetrievalService:服务发现,用于获取当前 leader 的地址。目前用到服务发现的组件有 ResourceManager、Dispatcher、JobManager、ClusterRestEndpoint。
-
LeaderElection:选举服务,从多个候选者中选出一个作为 leader。用到选举服务的同样是 ResourceManager、Dispatcher、JobManager、ClusterRestEndpoint 这四个。
-
CheckpointRecoveryFactory:Checkpoint 恢复组件的工厂类,提供了创建 CompletedCheckpointStore 和 CheckpointIDCounter 的方法。CompletedCheckpointStore 是用于存储已完成的 checkpoint 的元信息,CheckpointIDCounter 是用于生成 checkpoint ID。
-
ExecutionPlanStore:用于存储执行计划。
-
JobResultStore:用于存储作业结果,这里有两种状态,一种是 dirty,表示作业没有被完全清理,另一种是 clean,表示作业清理工作已经执行完成了。
-
BlobStore:存储作业运行期间的一些二进制文件。
选举服务
Flink 的选举是依靠 LeaderElection 和 LeaderContender 配合完成的。LeaderElection 是 LeaderElectionService 的代理接口,提供了注册候选者、确认 leader 和 判断候选者是否是 leader 三个接口。LeaderContender 则是用来表示候选者对象。当一个 LeaderContender 当选 leader 后,LeaderElectionService 会为其生成一个 leaderSessionId,LeaderContender 会调用 confirmLeadershipAsync 发布自己的地址。选举服务的具体实现在 LeaderElectionDriver 接口中。
服务发现
服务发现的作用是获取各组件的 leader 地址。服务发现依赖 LeaderRetrievalService 和 LeaderRetrievalListener。LeaderRetrievalService 可以启动一个监听,当有新的 leader 当选时,会调用 LeaderRetrievalListener 的 notifyLeaderAddress 方法。
信息保存
当 leader 发生切换时,新的 leader 需要获取到旧 leader 存储的信息,这就需要旧 leader 把这些信息存在一个公共的存储上。它可以是 ZooKeeper 或 Kubernetes 的存储,也可以是分布式文件系统的存储。
基于 ZooKeeper 的 HA
选举服务
前面我们提到了选举服务主要依赖 LeaderElection 和 LeaderContender 配合完成。我们就以 JobManager 为例,看一下机遇 ZooKeeper 的选举流程的具体实现。
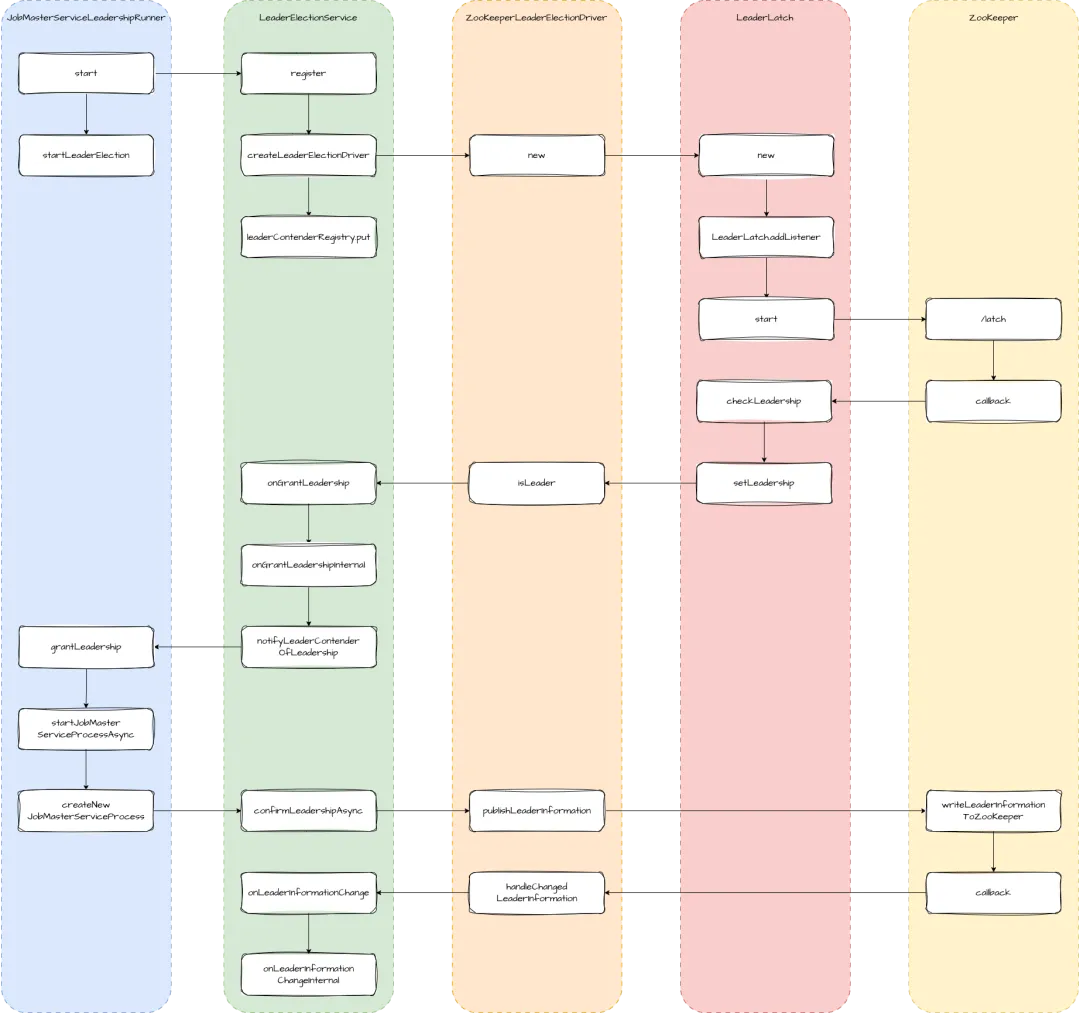
图中 JobMasterServiceLeadershipRunner 是 LeaderContender 的实现类。在启动服务时,会向 LeaderElection 注册自己的信息,实际执行者是 DefaultLeaderElectionService。它先创建了 LeaderElectionDriver,然后将 LeaderContender 保存在 leaderContenderRegistry 中。选举的核心逻辑封装在 LeaderElectionDriver 中。
在创建 LeaderElectionDriver 时,会创建 LeaderLatch 对象和 TreeCache 对象, LeaderLatch 封装了与 ZooKeeper 关联的回调,会接收一个 LeaderElectionDriver 作为监听。TreeCache 主要用于监听 ZooKeeper 中 leader 节点的变更。
publicZooKeeperLeaderElectionDriver(
CuratorFramework curatorFramework, LeaderElectionDriver.Listener leaderElectionListener)
throws Exception {
...
this.leaderLatch = new LeaderLatch(curatorFramework, ZooKeeperUtils.getLeaderLatchPath());
this.treeCache =
ZooKeeperUtils.createTreeCache(
curatorFramework,
"/",
new ZooKeeperLeaderElectionDriver.ConnectionInfoNodeSelector());
treeCache
.getListenable()
.addListener(
(client, event) -> {
switch (event.getType()) {
case NODE_ADDED:
case NODE_UPDATED:
Preconditions.checkNotNull(
event.getData(),
"The ZooKeeper event data must not be null.");
handleChangedLeaderInformation(event.getData());
break;
case NODE_REMOVED:
Preconditions.checkNotNull(
event.getData(),
"The ZooKeeper event data must not be null.");
handleRemovedLeaderInformation(event.getData().getPath());
break;
}
});
leaderLatch.addListener(this);
...
leaderLatch.start();
treeCache.start();
}
我们进入到 LeaderLatch 的 start 方法。它的内部是在 ZooKeeper 上创建 latch-xxx 节点。xxx 是当前 LeaderLatch 的 ID,它由 ZooKeeper 生成,ID 最小的当选 Leader。
privatevoidcheckLeadership(List<String> children)throws Exception {
if (this.debugCheckLeaderShipLatch != null) {
this.debugCheckLeaderShipLatch.await();
}
String localOurPath = (String)this.ourPath.get();
List<String> sortedChildren = LockInternals.getSortedChildren("latch-", sorter, children);
int ourIndex = localOurPath != null ? sortedChildren.indexOf(ZKPaths.getNodeFromPath(localOurPath)) : -1;
this.log.debug("checkLeadership with id: {}, ourPath: {}, children: {}", new Object[]{this.id, localOurPath, sortedChildren});
if (ourIndex < 0) {
this.log.error("Can't find our node. Resetting. Index: " + ourIndex);
this.reset();
} elseif (ourIndex == 0) {
this.lastPathIsLeader.set(localOurPath);
this.setLeadership(true);
} else {
this.setLeadership(false);
String watchPath = (String)sortedChildren.get(ourIndex - 1);
Watcher watcher = new Watcher() {
publicvoidprocess(WatchedEvent event){
if (LeaderLatch.this.state.get() == LeaderLatch.State.STARTED && event.getType() == EventType.NodeDeleted) {
try {
LeaderLatch.this.getChildren();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ThreadUtils.checkInterrupted(ex);
LeaderLatch.this.log.error("An error occurred checking the leadership.", ex);
}
}
}
};
BackgroundCallback callback = new BackgroundCallback() {
publicvoidprocessResult(CuratorFramework client, CuratorEvent event)throws Exception {
if (event.getResultCode() == Code.NONODE.intValue()) {
LeaderLatch.this.getChildren();
}
}
};
((ErrorListenerPathable)((BackgroundPathable)this.client.getData().usingWatcher(watcher)).inBackground(callback)).forPath(ZKPaths.makePath(this.latchPath, watchPath));
}
}
当选 Leader 后,会回调 LeaderElectionDriver 的 isLeader 方法,如果未当选,则继续监听 latch 节点的变更。isLeader 会继续回调 LeaderElection 的 onGrantLeadership 方法,接着调用 LeaderContender 的 grantLeadership。这时会启动 JobMaster 服务,然后调用 LeaderElection 的 confirmLeadershipAsync 来确认当选成功。确认的过程是由 LeaderElectionDriver 来执行的。主要作用是把当前 leader 的信息写回到 ZooKeeper 的 connection_info 节点。
publicvoidpublishLeaderInformation(String componentId, LeaderInformation leaderInformation){
Preconditions.checkState(running.get());
if (!leaderLatch.hasLeadership()) {
return;
}
final String connectionInformationPath =
ZooKeeperUtils.generateConnectionInformationPath(componentId);
LOG.debug(
"Write leader information {} for component '{}' to {}.",
leaderInformation,
componentId,
ZooKeeperUtils.generateZookeeperPath(
curatorFramework.getNamespace(), connectionInformationPath));
try {
ZooKeeperUtils.writeLeaderInformationToZooKeeper(
leaderInformation,
curatorFramework,
leaderLatch::hasLeadership,
connectionInformationPath);
} catch (Exception e) {
leaderElectionListener.onError(e);
}
}
服务发现
梳理完选举服务的源码后,我们再来看一下服务发现的过程。我们以 TaskManager 获取 JobManager 的 leader 为例。
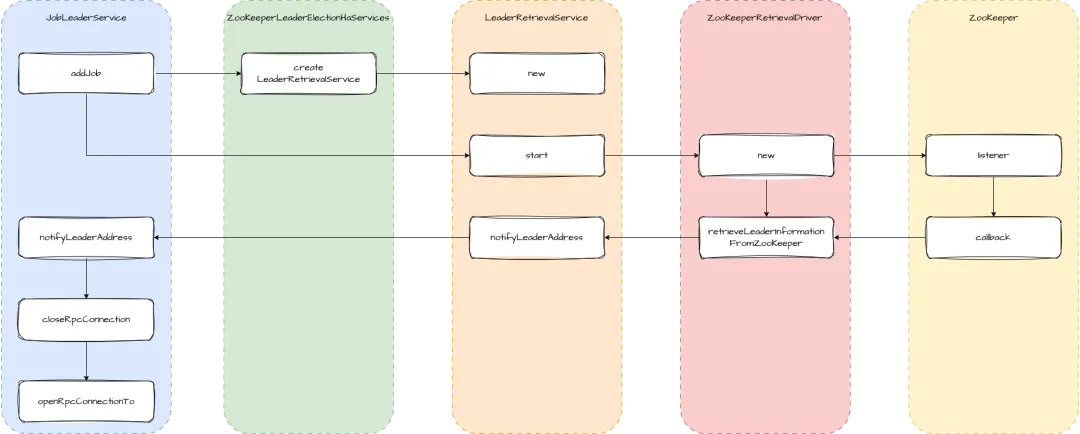
当我们往 TaskManager 添加任务时,会调用 JobLeaderService 的 addJob 方法。这里会先获取 LeaderRetrieval,然后调用 start 方法注册 LeaderRetrievalListener 监听,并创建 LeaderRetrievalDriver。在 LeaderRetrievalDriver 中主要是向 ZooKeeper 注册 connection_info 节点的变更。
如果发生变更,ZooKeeper 会回调 LeaderRetrievalDriver.retrieveLeaderInformationFromZooKeeper 方法。我们从 ZooKeeper 获取到 leader 的地址和 sessionId 后,就回调 LeaderRetrievalService.notifyLeaderAddress 方法。最终调用到 JobLeaderService 的 notifyLeaderAddress 方法,这个方法中就是断开与旧 leader 的连接,增加与新 leader 的连接。
信息保存
最后我们再来看信息保存相关的源码。在 JobManager 完成一次 Checkpoint 时,会执行 CheckpointCoordinator.completePendingCheckpoint 方法,跟随调用链路可以找到 ZooKeeperStateHandleStore.addAndLock 方法,这里会把状态写入到文件系统中,然后把文件路径保存在 ZooKeeper 中。
public RetrievableStateHandle<T> addAndLock(String pathInZooKeeper, T state)
throws PossibleInconsistentStateException, Exception {
checkNotNull(pathInZooKeeper, "Path in ZooKeeper");
checkNotNull(state, "State");
final String path = normalizePath(pathInZooKeeper);
final Optional<Stat> maybeStat = getStat(path);
if (maybeStat.isPresent()) {
if (isNotMarkedForDeletion(maybeStat.get())) {
thrownew AlreadyExistException(
String.format("ZooKeeper node %s already exists.", path));
}
Preconditions.checkState(
releaseAndTryRemove(path),
"The state is marked for deletion and, therefore, should be deletable.");
}
final RetrievableStateHandle<T> storeHandle = storage.store(state);
finalbyte[] serializedStoreHandle = serializeOrDiscard(storeHandle);
try {
writeStoreHandleTransactionally(path, serializedStoreHandle);
return storeHandle;
} catch (KeeperException.NodeExistsException e) {
// Transactions are not idempotent in the curator version we're currently using, so it
// is actually possible that we've re-tried a transaction that has already succeeded.
// We've ensured that the node hasn't been present prior executing the transaction, so
// we can assume that this is a result of the retry mechanism.
return storeHandle;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (indicatesPossiblyInconsistentState(e)) {
thrownew PossibleInconsistentStateException(e);
}
// In case of any other failure, discard the state and rethrow the exception.
storeHandle.discardState();
throw e;
}
}
至此,基于 ZooKeeper 的 HA 逻辑我们就梳理完了。从 1.12 版本开始,Flink 还支持了 Kubernetes 高可用,下面我们再来一下它是如何实现的。
基于 Kubernetes 的 HA
选举服务
通过前面的学习,我们已经了解到,选举的主要逻辑是在 LeaderElectionDriver 中,因此,我们直接来看 KubernetesLeaderElectionDriver 的逻辑即可。创建 KubernetesLeaderElectionDriver 时,创建并启动了 KubernetesLeaderElector。这个类似于 ZooKeeper 逻辑中 LeaderLatch,会跟 Kubernetes 底层的选举逻辑交互,同时注册监听。
publicKubernetesLeaderElector(
NamespacedKubernetesClient kubernetesClient,
KubernetesLeaderElectionConfiguration leaderConfig,
LeaderCallbackHandler leaderCallbackHandler,
ExecutorService executorService){
this.kubernetesClient = kubernetesClient;
this.leaderElectionConfig =
new LeaderElectionConfigBuilder()
.withName(leaderConfig.getConfigMapName())
.withLeaseDuration(leaderConfig.getLeaseDuration())
.withLock(
new ConfigMapLock(
new ObjectMetaBuilder()
.withNamespace(kubernetesClient.getNamespace())
.withName(leaderConfig.getConfigMapName())
// Labels will be used to clean up the ha related
// ConfigMaps.
.withLabels(
KubernetesUtils.getConfigMapLabels(
leaderConfig.getClusterId()))
.build(),
leaderConfig.getLockIdentity()))
.withRenewDeadline(leaderConfig.getRenewDeadline())
.withRetryPeriod(leaderConfig.getRetryPeriod())
.withReleaseOnCancel(true)
.withLeaderCallbacks(
new LeaderCallbacks(
leaderCallbackHandler::isLeader,
leaderCallbackHandler::notLeader,
newLeader ->
LOG.info(
"New leader elected {} for {}.",
newLeader,
leaderConfig.getConfigMapName())))
.build();
this.executorService = executorService;
LOG.info(
"Create KubernetesLeaderElector on lock {}.",
leaderElectionConfig.getLock().describe());
}
选举成功后,会回调 LeaderElectionListener.onGrantLeadership 方法。后续的调用链路还是会调用到 KubernetesLeaderElectionDriver.publishLeaderInformation 方法。这个方法是把 leader 信息写到 Kubernetes 的 configMap 中。
publicvoidpublishLeaderInformation(String componentId, LeaderInformation leaderInformation){
Preconditions.checkState(running.get());
try {
kubeClient
.checkAndUpdateConfigMap(
configMapName,
updateConfigMapWithLeaderInformation(componentId, leaderInformation))
.get();
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
leaderElectionListener.onError(e);
}
LOG.debug(
"Successfully wrote leader information {} for leader {} into the config map {}.",
leaderInformation,
componentId,
configMapName);
}
服务发现
服务发现的逻辑在 KubernetesLeaderRetrievalDriver 类中,在创建时,会将内部类 ConfigMapCallbackHandlerImpl 注册为监听回调类。
当 configMap 有新增或变更后,会回调 LeaderRetrievalService.notifyLeaderAddress 方法。
privateclassConfigMapCallbackHandlerImpl
implementsFlinkKubeClient.WatchCallbackHandler<KubernetesConfigMap> {
@Override
publicvoidonAdded(List<KubernetesConfigMap> configMaps){
// The ConfigMap is created by KubernetesLeaderElectionDriver with
// empty data. We don't really need to process anything unless the retriever was started
// after the leader election has already succeeded.
final KubernetesConfigMap configMap = getOnlyConfigMap(configMaps, configMapName);
final LeaderInformation leaderInformation = leaderInformationExtractor.apply(configMap);
if (!leaderInformation.isEmpty()) {
leaderRetrievalEventHandler.notifyLeaderAddress(leaderInformation);
}
}
@Override
publicvoidonModified(List<KubernetesConfigMap> configMaps){
final KubernetesConfigMap configMap = getOnlyConfigMap(configMaps, configMapName);
leaderRetrievalEventHandler.notifyLeaderAddress(
leaderInformationExtractor.apply(configMap));
}
...
}
信息保存
信息保存的逻辑和 ZooKeeper 也非常类似。即先把 state 保存在文件系统,然后把存储路径写到 Kubernetes 写到 configMap 中。具体可以看 KubernetesStateHandleStore.addAndLock 方法。
总结
本文我们一起梳理了 Flink 中 JobManager 的 HA 机制相关源码。目前 Flink 支持 ZooKeeper 和 Kubernetes 两种实现。在梳理过程中,我们以 JobManager 为例,其他几个用到高可用的服务的选举逻辑也是一样的。
 夜雨聆风
夜雨聆风





