NanoBot源代码详解-2:工具调用

调用工具
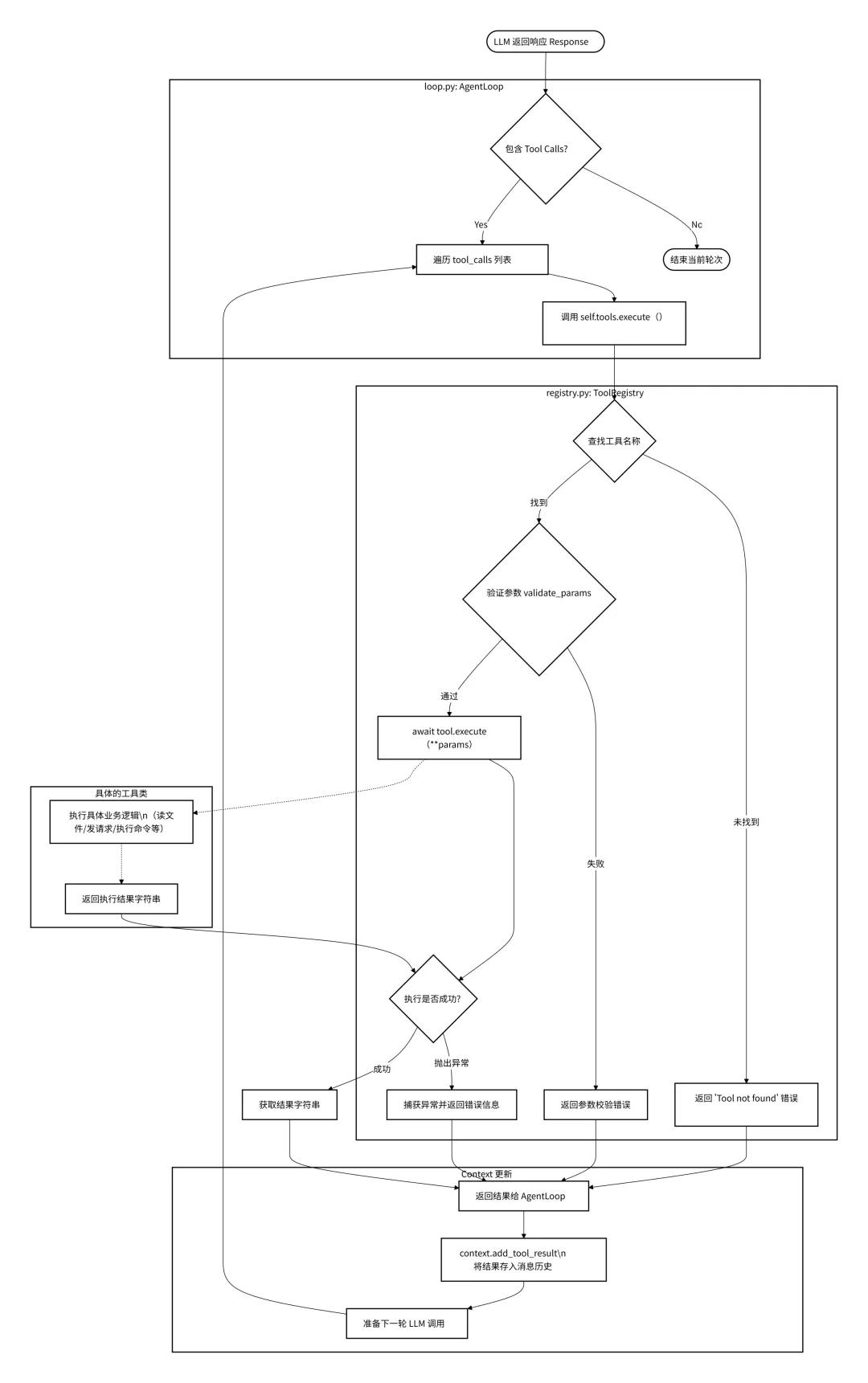
在loop.py中,当LLM返回的消息中包含tools_calls时,程序会遍历这些调用请求,并通过self.tools.execute()发起执行。
# loop.py L214-220for tool_call in response.tool_calls:# ... (日志记录)# 调用注册表执行工具 result = await self.tools.execute(tool_call.name, tool_call.arguments)# 将结果添加回消息历史 messages = self.context.add_tool_result( messages, tool_call.id, tool_call.name, result )然后在registry.py中,异步调用
# registry.py L38-60async def execute(self, name: str, params: dict[str, Any]) -> str: tool = self._tools.get(name) # 1. 查找工具if not tool:return f"Error: Tool '{name}' not found" try: errors = tool.validate_params(params) # 2. 参数验证if errors:return ... return await tool.execute(**params) # 3. 执行具体工具逻辑 except Exception as e:return f"Error executing {name}: {str(e)}" # 4. 异常捕获流程如下图:
系统源代码中已经自带了部分工具:
文件系统工具filesystem.py
包含工具 : ReadFileTool , WriteFileTool , EditFileTool , ListDirTool 主要使用python标准库pthlib.Path进行路径操作和文件IO。
消息发送工具message.py
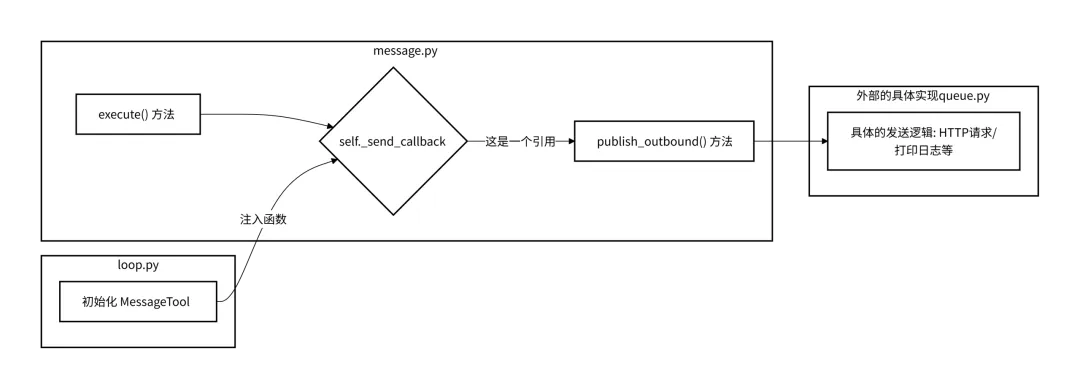
包含工具MessageTool 依赖nanobot.bus.events.OutboundMessage数据结构,通过回调函数self._send_callback(msg)将消息发送出去。 这个回调函数通常连接到系统的消息总线(MessageBus),最终由具体的适配器(如 Telegram Bot API 或 CLI 输出)处理发送逻辑。
这里回调时,先构造消息事件
msg = OutboundMessage( channel=target_channel, chat_id=target_chat_id, content=content )然后异步回调
await self._send_callback(msg)这个回调函数的发起在loop.py中,而实现在bus/queue.py中的publish_outbound方法中。
Sell命令执行工具shell.py
包含工具ExecTool,使用Python的asyncio库进行异步子进程管理。 调用 asyncio.create_subprocess_shell(command, …) 来启动 Shell 进程。 使用 process.communicate() 获取标准输出 (stdout) 和标准错误 (stderr)。_guard_command 方法,使用正则表达式( re 模块)拦截高危命令(如 rm -rf , format , dd 等)和路径遍历攻击。
也就是说如果你可以将某些命令加入黑名单deny_patterns,禁止其运行。也可以加入白名单allow_patterns
self.deny_patterns = deny_patterns or [ r"\brm\s+-[rf]{1,2}\b", # rm -r, rm -rf, rm -fr r"\bdel\s+/[fq]\b", # del /f, del /q r"\brmdir\s+/s\b", # rmdir /s r"\b(format|mkfs|diskpart)\b", # disk operations r"\bdd\s+if=", # dd r">\s*/dev/sd", # write to disk r"\b(shutdown|reboot|poweroff)\b", # system power r":\(\)\s*\{.*\};\s*:", # fork bomb ]基于正则的命令过滤 ( _guard_command ) 本质上是脆弱的,可以通过字符串拼接,编码等绕过。所以这里是有安全漏洞的。
子Agent生成工具spawn.py
用于创建后台任务(子Agent)。 它本身不执行复杂逻辑,而是代理调用 self._manager.spawn(...) 。 SubagentManager (在 nanobot.agent.subagent 中定义)负责实例化新的 AgentLoop 并在后台运行。
async def execute(self, task: str, label: str | None = None, **kwargs: Any) -> str:"""Spawn a subagent to execute the given task."""return await self._manager.spawn( task=task, label=label, origin_channel=self._origin_channel, origin_chat_id=self._origin_chat_id, )网络工具web.py
提供网络搜索和网页抓取功能。 包含工具 : WebSearchTool , WebFetchTool 使用 httpx (异步 HTTP 客户端)和 readability-lxml (网页内容提取)库。
WebSearchTool封装了Brave Search API,
async def execute(self, query: str, count: int | None = None, **kwargs: Any) -> str:if not self.api_key:return "Error: BRAVE_API_KEY not configured" try: n = min(max(count or self.max_results, 1), 10) async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client: r = await client.get("https://api.search.brave.com/res/v1/web/search", params={"q": query, "count": n}, headers={"Accept": "application/json", "X-Subscription-Token": self.api_key},timeout=10.0 ) r.raise_for_status() results = r.json().get("web", {}).get("results", []) ...如果需要封装其它的搜索引擎,可以在这里修改,比如我想将Brave修改成我喜欢的Tavily,就得修改这里的URL。如果需要定制化,可以在这里增加多种搜索引擎。
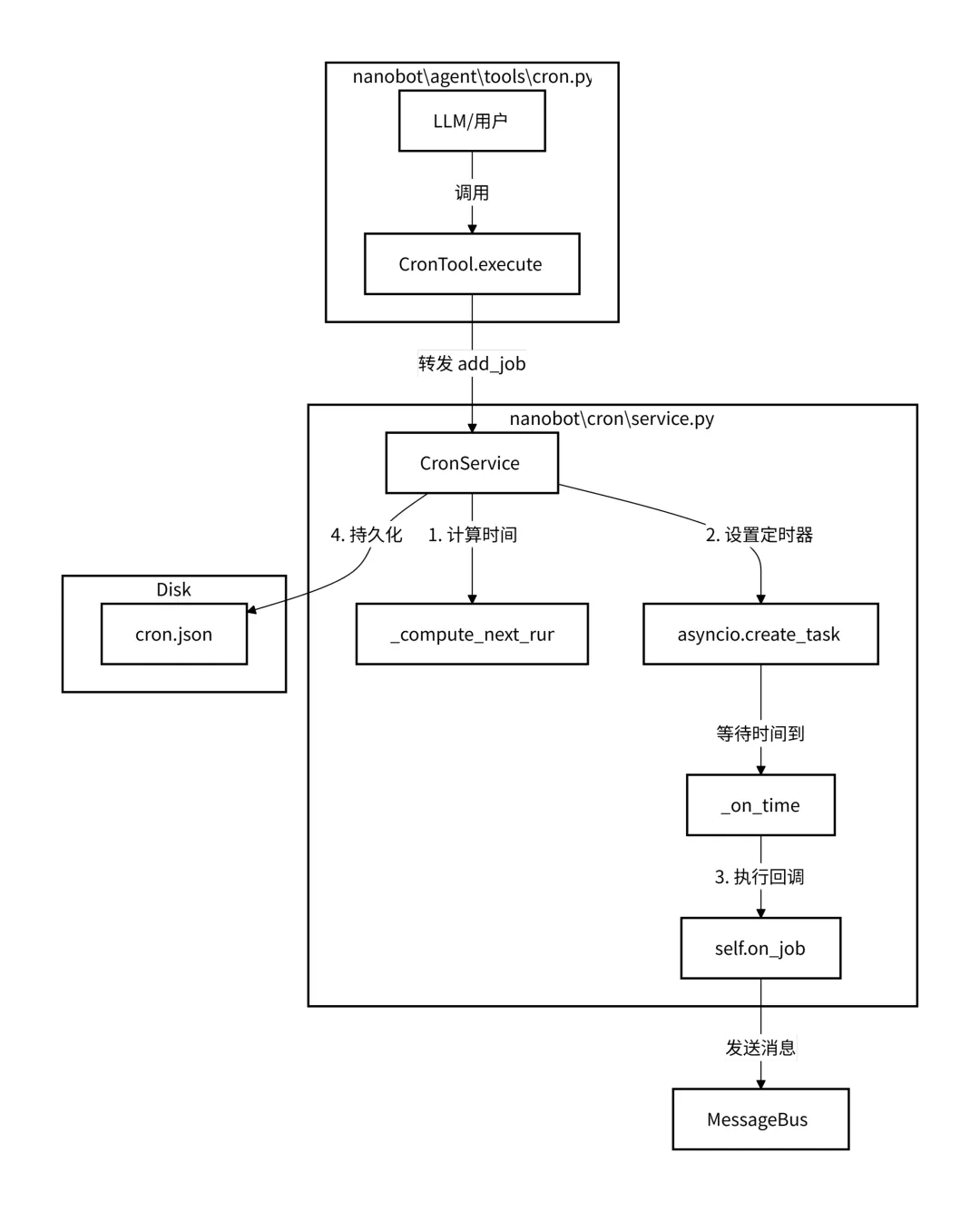
任务调度工具cron.py
定义了一个名为 CronTool 的工具类,该类赋予了 Agent 安排提醒和重复性任务的能力。它是 Nanobot 任务调度系统与 LLM 之间的桥梁。 这里只有_add_job(添加任务)、_list_jobs(列出任务)和_remove_job(删除任务)的函数,主要是管理任务。而具体的实现在 nanobat/cron/service.py中CronService。
 夜雨聆风
夜雨聆风





