【Dubbo】服务导出源码分析
前言
前面讨论了Dubbo与Spring的整合原理,今天讨论一下Dubbo服务导出流程
总体调用关系
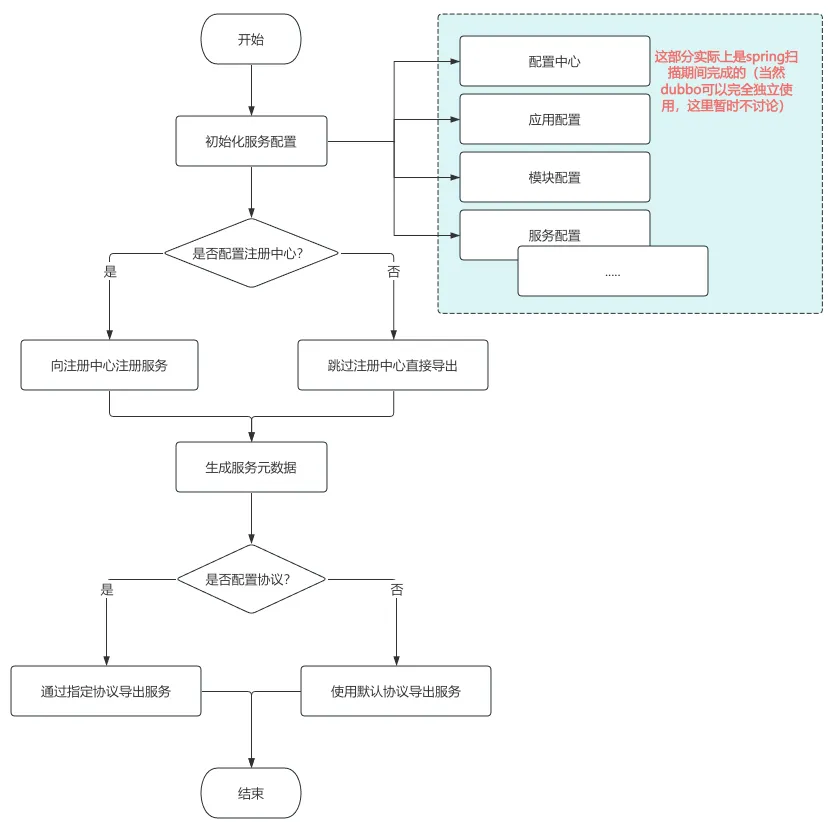
上述流程为整体导出过程的一个粗略架构图,后续会展开介绍详细流程
核心源码分析
调用时序图
时序图来自官方:https://cn.dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/overview/mannual/java-sdk/reference-manual/architecture/code-architecture/,我本地的代码是Dubbo3.0,跟这个有一些差异,但是整体来说区别不是非常大,不影响理解。
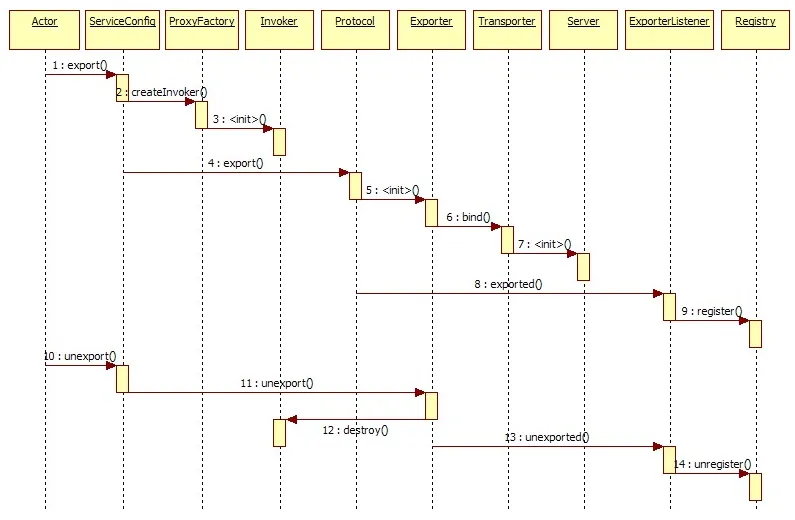
调用入口
上文中介绍到了在启动过程中注册了两个关键的监听器
DubboDeployApplicationListener,我们这里服务导出就从这个监听器开始
注册入口org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.util.DubboBeanUtils#registerCommonBeans
staticvoidregisterCommonBeans(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {// 省略无关代码// register ApplicationListeners,重点看这个 registerInfrastructureBean(registry, DubboDeployApplicationListener.class.getName(), DubboDeployApplicationListener.class);// 。。。。 }既然是监听器,那我们首先是应该看看它监听了什么?

上图可以看出,它实现了Spring自带的事件ApplicationContextEvent,这个事件主要是在Spring容器启动生命周期中会发送各类事件,用于用户根据需要进行扩展。Dubbo服务的导出主要就是依赖了其中两个事件。这里补充下ApplicationContextEvent的子类:

接下来回到正文,看看监听器DubboDeployApplicationListener具体实现逻辑,重点看org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.context.DubboDeployApplicationListener#onApplicationEvent方法:
publicvoidonApplicationEvent(ApplicationContextEvent event) {if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) { onContextRefreshedEvent((ContextRefreshedEvent) event); } elseif (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent) { onContextClosedEvent((ContextClosedEvent) event); }}这个监听器主要是用了Spring的ContextRefreshedEvent事件用于导出服务,实现了ContextClosedEvent用于取消导出服务,先来看看onContextRefreshedEvent源码
privatevoidonContextRefreshedEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {// 获取部署器(dubbo3.0对应用、模块都做了非常大的升级,这里先不深究)ModuleDeployerdeployer= moduleModel.getDeployer(); Assert.notNull(deployer, "Module deployer is null");// start module,导出服务(异步或者同步,根据配置),重点方法接着看CompletableFuturefuture= deployer.start();// 如果配置了不是异步导出,则等待导出完成if (!deployer.isBackground()) {try { future.get(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { logger.warn("Interrupted while waiting for dubbo module start: " + e.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn("An error occurred while waiting for dubbo module start: " + e.getMessage(), e); } }}导出&引用入口
接着看deployer.start()做了什么,代码位置
org.apache.dubbo.config.deploy.DefaultModuleDeployer#start
publicsynchronized CompletableFuture start()throws IllegalStateException {// 判断是否在启动中或者已经启动完成if (isStarting() || isStarted()) {return startFuture; }// 标记导出状态,发布事件 onModuleStarting(); startFuture = newCompletableFuture();// 应用初始化(这个方法也做了非常多事情,很重要,后续单独讨论,比如配置中心初始化,元数据初始化。。。) applicationDeployer.initialize();// initialize,加载最新配置,标记是否异步导出或引入 initialize();// export services,导出服务,重点来了 exportServices();// prepare application instanceif (hasExportedServices()) { applicationDeployer.prepareApplicationInstance(); }// refer services,引用服务,这个下一步讨论 referServices();// 等待导出、引用完成,然后回收一些用于启动服务的一些线程资源 executorRepository.getSharedExecutor().submit(() -> {// wait for export finish waitExportFinish();// wait for refer finish waitReferFinish(); onModuleStarted(startFuture); });return startFuture; }导出流程
导出主要是org.apache.dubbo.config.deploy.DefaultModuleDeployer#exportServices方法,我们重点看看:
第一步拿到所有的待导出server,循环调用
privatevoidexportServices() {// 从配置管理器拿到所有的待导出服务for (ServiceConfigBase sc : configManager.getServices()) {// 导出 exportServiceInternal(sc); }}接着看导出exportServiceInternal方法
privatevoidexportServiceInternal(ServiceConfigBase sc) { ServiceConfig<?> serviceConfig = (ServiceConfig<?>) sc;// 判断配置是否是最新的,不是的话重新刷新一些,这里回去环境变量,外部配置等读取最新配置,不是重点,这里不讨论if (!serviceConfig.isRefreshed()) { serviceConfig.refresh(); }// 已经导出就直接返回if (sc.isExported()) {return; }// 判断是否是异步导出if (exportAsync || sc.shouldExportAsync()) {// 线程池管理器ExecutorServiceexecutor= executorRepository.getServiceExportExecutor(); CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {try {if (!sc.isExported()) {// 导出 sc.exportOnly(); exportedServices.add(sc); } } catch (Throwable t) { logger.error(getIdentifier() + " export async catch error : " + t.getMessage(), t); } }, executor); asyncExportingFutures.add(future); } else {if (!sc.isExported()) { sc.exportOnly(); exportedServices.add(sc); } } }继续看exportOnly方法,代码位置
org.apache.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig#exportOnly
publicsynchronizedvoidexportOnly() {if (this.exported) {return; }// 保证配置是最新的if (!this.isRefreshed()) {this.refresh(); }// 是否需要导出if (this.shouldExport()) {// 初始化监听器this.init();if (shouldDelay()) {// 延迟导出 doDelayExport(); } else {// 同步导出 doExport(); } }}延迟导出org.apache.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig#doDelayExport
protectedvoiddoDelayExport() {// 实际上是起了个延迟任务,根据用于配置的延迟时间进行导出服务 DELAY_EXPORT_EXECUTOR.schedule(() -> {try {// 导出 doExport(); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Failed to export service config: " + interfaceName, e); } }, getDelay(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}接着看org.apache.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig#doExport
protectedsynchronizedvoiddoExport() {if (unexported) {thrownewIllegalStateException("The service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " has already unexported!"); }if (exported) {return; }if (StringUtils.isEmpty(path)) { path = interfaceName; }// 导出 doExportUrls();// 缓存已经导出的服务 exported(); }接着看org.apache.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig#doExportUrls
privatevoiddoExportUrls() {// 获取模块服务仓库ModuleServiceRepositoryrepository= getScopeModel().getServiceRepository();// 获取服务描述器,一个服务里面会有很多歌方法,每个方法可能有自己的配置ServiceDescriptorserviceDescriptor= repository.registerService(getInterfaceClass());// 服务提供者模型 providerModel = newProviderModel(getUniqueServiceName(), ref, serviceDescriptor,this, getScopeModel(), serviceMetadata);// 注册到模块服务仓库 repository.registerProvider(providerModel);// 使用loadRegistries获取到所有的注册中心地址,用户可能会配置多个注册中心// registry://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?REGISTRY_CLUSTER=registryConfig&application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&dubbo=2.0.2&pid=13403®istry=zookeeper×tamp=1767344233494 List<URL> registryURLs = ConfigValidationUtils.loadRegistries(this, true);// 遍历当前服务的协议配置,通过doExportUrlsFor1Protocol按照每个协议分别注册到注册中心(注意注册中心可以是多个)for (ProtocolConfig protocolConfig : protocols) {StringpathKey= URL.buildKey(getContextPath(protocolConfig) .map(p -> p + "/" + path) .orElse(path), group, version);// 如果用于声明了路径,则需要再次用新路径注册服务 repository.registerService(pathKey, interfaceClass);// 导出服务,重点,注意这里的protocol是registry://开头 doExportUrlsFor1Protocol(protocolConfig, registryURLs); }}接着看org.apache.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig#doExportUrlsFor1Protocol
privatevoiddoExportUrlsFor1Protocol(ProtocolConfig protocolConfig, List<URL> registryURLs) {// 得到协议配置 Map<String, String> map = buildAttributes(protocolConfig);//init serviceMetadata attachments serviceMetadata.getAttachments().putAll(map);// 构建url,类似这样dubbo://192.168.1.101:20880/org.apache.dubbo.demo.UserService?anyhost=true&application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&background=false&bind.ip=192.168.1.101&bind.port=20880&deprecated=false&dubbo=2.0.2&dynamic=true&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.UserService&metadata-type=remote&methods=getUser&pid=8169&release=&side=provider×tamp=1767277014048URLurl= buildUrl(protocolConfig, registryURLs, map);// 导出url exportUrl(url, registryURLs);}继续看org.apache.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig#exportUrl
privatevoidexportUrl(URL url, List<URL> registryURLs) {// 范围Stringscope= url.getParameter(SCOPE_KEY);// don't export when none is configuredif (!SCOPE_NONE.equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) {// 本地配置不用导出到远程// export to local if the config is not remote (export to remote only when config is remote)if (!SCOPE_REMOTE.equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) { exportLocal(url); }// export to remote if the config is not local (export to local only when config is local)if (!SCOPE_LOCAL.equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) {// 远程导出,重点方法 url = exportRemote(url, registryURLs);// 发布事件 MetadataUtils.publishServiceDefinition(url); } }this.urls.add(url); }分析org.apache.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig#exportRemote
private URL exportRemote(URL url, List<URL> registryURLs) {if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(registryURLs)) {// 注册中心,这里其实有两个,// service-discovery-registry://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?REGISTRY_CLUSTER=registryConfig&application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&dubbo=2.0.2&pid=8299®istry=zookeeper×tamp=1767277773610// registry://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?REGISTRY_CLUSTER=registryConfig&application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&dubbo=2.0.2&pid=8299®istry=zookeeper×tamp=1767277773610for (URL registryURL : registryURLs) {if (SERVICE_REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(registryURL.getProtocol())) { url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(SERVICE_NAME_MAPPING_KEY, "true"); }//if protocol is only injvm ,not registerif (LOCAL_PROTOCOL.equalsIgnoreCase(url.getProtocol())) {continue; }// dubbo://xxx url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(DYNAMIC_KEY, registryURL.getParameter(DYNAMIC_KEY));URLmonitorUrl= ConfigValidationUtils.loadMonitor(this, registryURL);if (monitorUrl != null) { url = url.putAttribute(MONITOR_KEY, monitorUrl); }// For providers, this is used to enable custom proxy to generate invokerStringproxy= url.getParameter(PROXY_KEY);if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(proxy)) { registryURL = registryURL.addParameter(PROXY_KEY, proxy); } // 讲dubbo://开头的url添加到当前的注册中心URL上。然后调用doExportUrl导出 doExportUrl(registryURL.putAttribute(EXPORT_KEY, url), true); } } else {if (MetadataService.class.getName().equals(url.getServiceInterface())) { localMetadataService.setMetadataServiceURL(url); }if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Export dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " to url " + url); } doExportUrl(url, true); }return url;}接着看org.apache.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig#doExportUrl
privatevoiddoExportUrl(URL url, boolean withMetaData) {// 生成动态代理invoker对象,这里的代理非常重要,后续单独写一个文档,立一个flag在这里 Invoker<?> invoker = proxyFactory.getInvoker(ref, (Class) interfaceClass, url);if (withMetaData) { invoker = newDelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker(invoker, this); }// 通过protocol进行导出操作,注意这里的protocol是一个动态代理Adaptive。底层通过SPI拿到的registryProtocol,然后调用export Exporter<?> exporter = protocolSPI.export(invoker); exporters.add(exporter);}这里的导出是一个dubbo的动态代理机制,会调用到如下方法,实际逻辑即使根据url上配置的协议通过spi获取真正的protocol
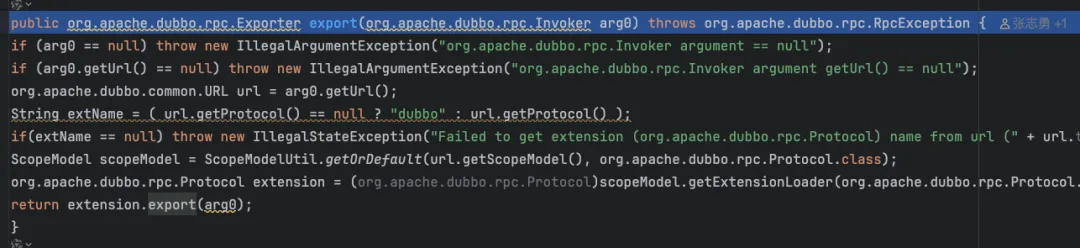
通过上述的动态代理会调用到org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryProtocol#export,因为org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol文件配置的是org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.InterfaceCompatibleRegistryProtocol。代码如下:
public <T> Exporter<T> export(final Invoker<T> originInvoker)throws RpcException {// 实际的注册地址 zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?REGISTRY_CLUSTER=registryConfig&application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&dubbo=2.0.2&pid=13600×tamp=1767345767765URLregistryUrl= getRegistryUrl(originInvoker);// 需要导出的服务地址 dubbo://192.168.1.101:20880/org.apache.dubbo.demo.UserService?anyhost=true&application=dubbo-demo-annotation-provider&background=false&bind.ip=192.168.1.101&bind.port=20880&deprecated=false&dubbo=2.0.2&dynamic=true&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.UserService&metadata-type=remote&methods=getUser&pid=13600&release=&service-name-mapping=true&side=provider×tamp=1767345772348URLproviderUrl= getProviderUrl(originInvoker);// Subscribe the override data// FIXME When the provider subscribes, it will affect the scene : a certain JVM exposes the service and call// the same service. Because the subscribed is cached key with the name of the service, it causes the// subscription information to cover.// 生成监听器,主要为了动态配置变化,如果有监听到就覆盖原有的finalURLoverrideSubscribeUrl= getSubscribedOverrideUrl(providerUrl);finalOverrideListeneroverrideSubscribeListener=newOverrideListener(overrideSubscribeUrl, originInvoker); Map<URL, NotifyListener> overrideListeners = getProviderConfigurationListener(providerUrl).getOverrideListeners(); overrideListeners.put(registryUrl, overrideSubscribeListener); providerUrl = overrideUrlWithConfig(providerUrl, overrideSubscribeListener);//export invoker 启动当前服务的nettyserverfinal ExporterChangeableWrapper<T> exporter = doLocalExport(originInvoker, providerUrl);// url to registry 注册到注册中心finalRegistryregistry= getRegistry(registryUrl);// 确定最终需要保存到注册中心的地址finalURLregisteredProviderUrl= getUrlToRegistry(providerUrl, registryUrl);// decide if we need to delay publish 延迟注册booleanregister= providerUrl.getParameter(REGISTER_KEY, true);if (register) { register(registry, registeredProviderUrl); }// register stated url on provider model registerStatedUrl(registryUrl, registeredProviderUrl, register); exporter.setRegisterUrl(registeredProviderUrl); exporter.setSubscribeUrl(overrideSubscribeUrl);// Deprecated! Subscribe to override rules in 2.6.x or before.// 订阅配置中心关于注册中心的配置变更 registry.subscribe(overrideSubscribeUrl, overrideSubscribeListener);// 发送通知 notifyExport(exporter);//Ensure that a new exporter instance is returned every time exportreturnnewDestroyableExporter<>(exporter); }先来看看org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryProtocol#doLocalExport
private <T> ExporterChangeableWrapper<T> doLocalExport(final Invoker<T> originInvoker, URL providerUrl) {Stringkey= getCacheKey(originInvoker);// 这里继续调用protocol.export导出,这里还是一个Dubbo的Aop,是DubboProtocol的return (ExporterChangeableWrapper<T>) bounds.computeIfAbsent(key, s -> { Invoker<?> invokerDelegate = newInvokerDelegate<>(originInvoker, providerUrl);returnnewExporterChangeableWrapper<>((Exporter<T>) protocol.export(invokerDelegate), originInvoker); }); }这里继续调用protocol.export导出,这里还是一个Dubbo的Aop,是DubboProtocol的一一堆Warpper,大概是这样的
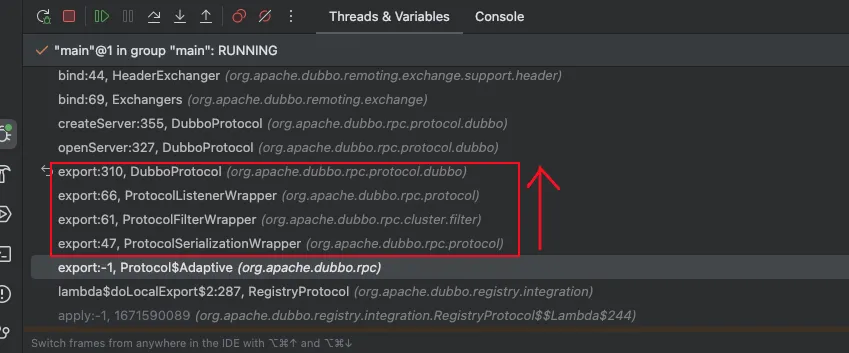
用一个图的话,这里的调用关系是这样,这个是在加载SPI时就根据Order进行排好序的,类似Warpper的东西都是这个套路,一层包一层的调用:
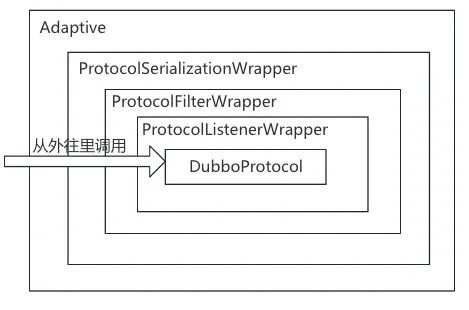
-
• ProtocolSerializationWrapper:主要做资源回收 -
• ProtocolFilterWrapper:构建过滤器链,这个比较重要,真正调用的时候会请求会过这些过滤器 -
• ProtocolListenerWrapper:构建一些监听器,这几个其实warpper没有做太多事情过完了上面的几个Wrapper,接着会走到真正注册的DubboProtocol的export,代码位置org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol#export
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker)throws RpcException {URLurl= invoker.getUrl();// export service.Stringkey= serviceKey(url); DubboExporter<T> exporter = newDubboExporter<T>(invoker, key, exporterMap); exporterMap.put(key, exporter);// 存根验证//export an stub service for dispatching eventBooleanisStubSupportEvent= url.getParameter(STUB_EVENT_KEY, DEFAULT_STUB_EVENT);BooleanisCallbackservice= url.getParameter(IS_CALLBACK_SERVICE, false);if (isStubSupportEvent && !isCallbackservice) {StringstubServiceMethods= url.getParameter(STUB_EVENT_METHODS_KEY);if (stubServiceMethods == null || stubServiceMethods.length() == 0) {if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn(newIllegalStateException("consumer [" + url.getParameter(INTERFACE_KEY) +"], has set stubproxy support event ,but no stub methods founded.")); } } }// 启动server端 openServer(url); optimizeSerialization(url);return exporter; }接着看org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol#openServer
privatevoidopenServer(URL url) {// find server.Stringkey= url.getAddress();//client can export a service which's only for server to invokebooleanisServer= url.getParameter(IS_SERVER_KEY, true);// 如果服务启动过就不再启动了if (isServer) {ProtocolServerserver= serverMap.get(key);if (server == null) {synchronized (this) { server = serverMap.get(key);if (server == null) {// 创建server, serverMap.put(key, createServer(url)); }else { server.reset(url); } } } else {// server supports reset, use together with override server.reset(url); } }}调用exchange层创建服务,org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol#createServer,离真正的启动越来越近了
private ProtocolServer createServer(URL url) { url = URLBuilder.from(url)// send readonly event when server closes, it's enabled by default .addParameterIfAbsent(CHANNEL_READONLYEVENT_SENT_KEY, Boolean.TRUE.toString())// enable heartbeat by default .addParameterIfAbsent(HEARTBEAT_KEY, String.valueOf(DEFAULT_HEARTBEAT)) .addParameter(CODEC_KEY, DubboCodec.NAME) .build();Stringstr= url.getParameter(SERVER_KEY, DEFAULT_REMOTING_SERVER);if (str != null && str.length() > 0 && !url.getOrDefaultFrameworkModel().getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).hasExtension(str)) {thrownewRpcException("Unsupported server type: " + str + ", url: " + url); } ExchangeServer server;try {// 重点方法 server = Exchangers.bind(url, requestHandler); } catch (RemotingException e) {thrownewRpcException("Fail to start server(url: " + url + ") " + e.getMessage(), e); } str = url.getParameter(CLIENT_KEY);if (str != null && str.length() > 0) { Set<String> supportedTypes = url.getOrDefaultFrameworkModel().getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).getSupportedExtensions();if (!supportedTypes.contains(str)) {thrownewRpcException("Unsupported client type: " + str); } }DubboProtocolServerprotocolServer=newDubboProtocolServer(server); loadServerProperties(protocolServer);return protocolServer; }重点看Exchangers.bind(url, requestHandler)
publicstatic ExchangeServer bind(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler)throws RemotingException {if (url == null) {thrownewIllegalArgumentException("url == null"); }if (handler == null) {thrownewIllegalArgumentException("handler == null"); } url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.CODEC_KEY, "exchange");// 继续看return getExchanger(url).bind(url, handler);}getExchanger(url).bind(url, handler)
publicstatic Exchanger getExchanger(URL url) {Stringtype= url.getParameter(Constants.EXCHANGER_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_EXCHANGER);// 通过api获取当前的exchangerreturn url.getOrDefaultFrameworkModel().getExtensionLoader(Exchanger.class).getExtension(type);}接着到org.apache.dubbo.remoting.exchange.support.header.HeaderExchanger#bind
public ExchangeServer bind(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler)throws RemotingException {returnnewHeaderExchangeServer(Transporters.bind(url, newDecodeHandler(newHeaderExchangeHandler(handler)))); }接着调org.apache.dubbo.remoting.Transporters#bind(org.apache.dubbo.common.URL, org.apache.dubbo.remoting.ChannelHandler…)
publicstatic RemotingServer bind(URL url, ChannelHandler... handlers)throws RemotingException {if (url == null) {thrownewIllegalArgumentException("url == null"); }if (handlers == null || handlers.length == 0) {thrownewIllegalArgumentException("handlers == null"); } ChannelHandler handler;if (handlers.length == 1) { handler = handlers[0]; } else { handler = newChannelHandlerDispatcher(handlers); }return getTransporter(url).bind(url, handler);}继续调用getTransporter(url).bind(url, handler),这里回走到代理类,然后通过api获取真正的Transpoter
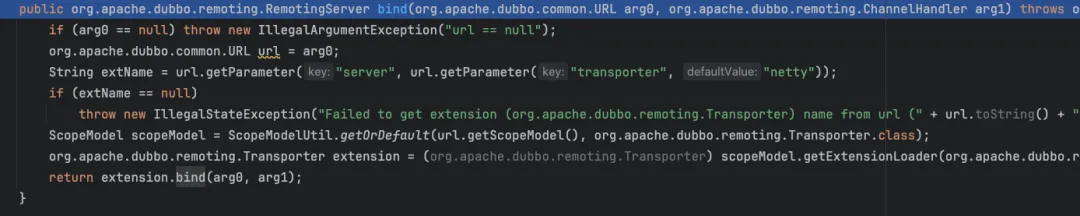
这里会走到org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4.NettyServer
publicNettyServer(URL url, ChannelHandler handler)throws RemotingException {// you can customize name and type of client thread pool by THREAD_NAME_KEY and THREADPOOL_KEY in CommonConstants.// the handler will be wrapped: MultiMessageHandler->HeartbeatHandler->handlersuper(ExecutorUtil.setThreadName(url, SERVER_THREAD_POOL_NAME), ChannelHandlers.wrap(handler, url));// read config before destroy serverShutdownTimeoutMills = ConfigurationUtils.getServerShutdownTimeout(getUrl().getOrDefaultModuleModel());}这里什么都没做,看父类,重点来了
publicAbstractServer(URL url, ChannelHandler handler)throws RemotingException {super(url, handler); executorRepository = url.getOrDefaultApplicationModel().getExtensionLoader(ExecutorRepository.class).getDefaultExtension(); localAddress = getUrl().toInetSocketAddress();// 服务端ipStringbindIp= getUrl().getParameter(Constants.BIND_IP_KEY, getUrl().getHost());// 端口intbindPort= getUrl().getParameter(Constants.BIND_PORT_KEY, getUrl().getPort());if (url.getParameter(ANYHOST_KEY, false) || NetUtils.isInvalidLocalHost(bindIp)) { bindIp = ANYHOST_VALUE; }// 声明InetSocketAddress bindAddress = newInetSocketAddress(bindIp, bindPort);this.accepts = url.getParameter(ACCEPTS_KEY, DEFAULT_ACCEPTS);try {// 真正启动服务 doOpen();if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Start " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " bind " + getBindAddress() + ", export " + getLocalAddress()); } } catch (Throwable t) {thrownewRemotingException(url.toInetSocketAddress(), null, "Failed to bind " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " on " + getLocalAddress() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); }// 创建线程池,为了后续回收资源 executor = executorRepository.createExecutorIfAbsent(url);}看doOpen,熟悉的代码来了
org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4.NettyServer#doOpen
protectedvoiddoOpen()throws Throwable { bootstrap = newServerBootstrap(); bossGroup = NettyEventLoopFactory.eventLoopGroup(1, "NettyServerBoss"); workerGroup = NettyEventLoopFactory.eventLoopGroup( getUrl().getPositiveParameter(IO_THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_IO_THREADS),"NettyServerWorker");finalNettyServerHandlernettyServerHandler=newNettyServerHandler(getUrl(), this); channels = nettyServerHandler.getChannels();booleankeepalive= getUrl().getParameter(KEEP_ALIVE_KEY, Boolean.FALSE); bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NettyEventLoopFactory.serverSocketChannelClass()) .option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, Boolean.TRUE) .childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, Boolean.TRUE) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, keepalive) .childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT) .childHandler(newChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@OverrideprotectedvoidinitChannel(SocketChannel ch)throws Exception {// FIXME: should we use getTimeout()?intidleTimeout= UrlUtils.getIdleTimeout(getUrl());NettyCodecAdapteradapter=newNettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyServer.this);if (getUrl().getParameter(SSL_ENABLED_KEY, false)) { ch.pipeline().addLast("negotiation", newSslServerTlsHandler(getUrl())); } ch.pipeline() .addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder()) .addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder()) .addLast("server-idle-handler", newIdleStateHandler(0, 0, idleTimeout, MILLISECONDS)) .addLast("handler", nettyServerHandler); } });// bindChannelFuturechannelFuture= bootstrap.bind(getBindAddress()); channelFuture.syncUninterruptibly(); channel = channelFuture.channel();}上面这段代码实际上就是启动了一个Netty服务,注入了Dubbo协议的序列化和反序列化编码器。这都是netty的内容了,Netty底层就是Nio了,后续慢慢在分享吧。其实到这里,服务启动就完成了。接着回到org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryProtocol#export的代码,调用doLocalexport完成服务启动后,进行服务注册。
首先是获取注册中心
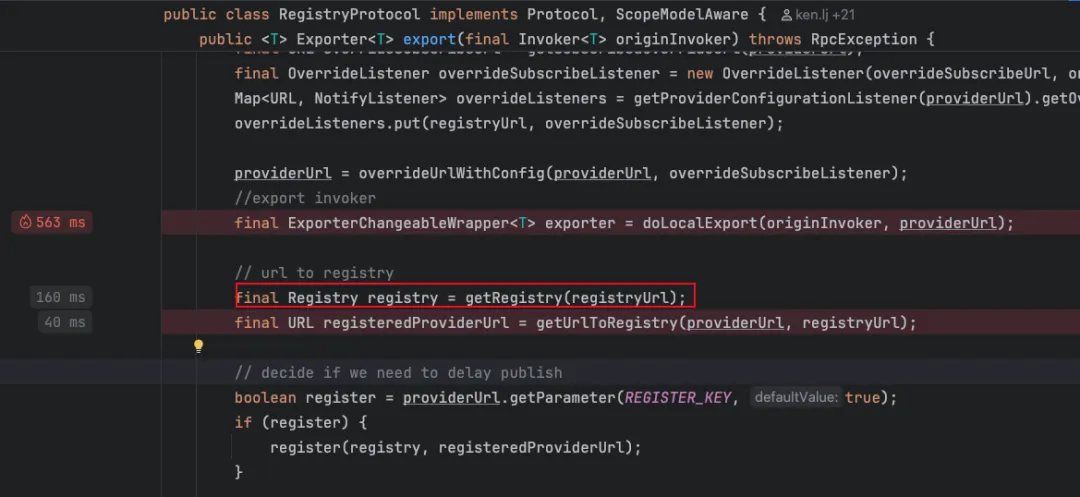
看看具体实现,代码位置
org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryProtocol#getRegistry
protected Registry getRegistry(final URL registryUrl) {// 使用SPI获取factory,然后获取注册器,默认配置是wrapper=org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryFactoryWrapperRegistryFactoryregistryFactory= ScopeModelUtil.getExtensionLoader(RegistryFactory.class, registryUrl.getScopeModel()).getAdaptiveExtension();return registryFactory.getRegistry(registryUrl); }这里SPI,由于我们配置的注册中心为zookeeper://xxx,所以这里根据registryFactory.getRegistry获取到的注册中心工厂则为ZookeeperRegistry,由于经过了Warpper包装所依返回的是ListenerRegistryWrapper
public Registry getRegistry(URL url) {returnnewListenerRegistryWrapper(registryFactory.getRegistry(url), Collections.unmodifiableList(url.getOrDefaultApplicationModel().getExtensionLoader(RegistryServiceListener.class) .getActivateExtension(url, "registry.listeners"))); }这样就获取到了注册中心,接下来就是真正的注册了
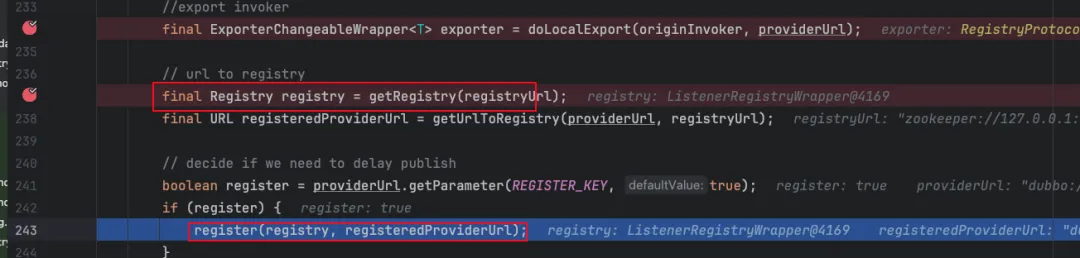
接着看register方法,一路调用会调用到org.apache.dubbo.registry.support.FailbackRegistry#register方法,直接看这里FailbackRegistry是ZookeeperRegistry的父类
publicvoidregister(URL url) {if (!acceptable(url)) { logger.info("URL " + url + " will not be registered to Registry. Registry " + url + " does not accept service of this protocol type.");return; }super.register(url); removeFailedRegistered(url); removeFailedUnregistered(url);try {// Sending a registration request to the server side// 重点方法,这里回调用实际实现类的注册方法 doRegister(url); } catch (Exception e) {// 异常处理先不看Throwablet= e;// If the startup detection is opened, the Exception is thrown directly.booleancheck= getUrl().getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true) && url.getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true) && !(url.getPort() == 0);booleanskipFailback= t instanceof SkipFailbackWrapperException;if (check || skipFailback) {if (skipFailback) { t = t.getCause(); }thrownewIllegalStateException("Failed to register " + url + " to registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); } else { logger.error("Failed to register " + url + ", waiting for retry, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); }// Record a failed registration request to a failed list, retry regularly addFailedRegistered(url); }}接着看最后的方法org.apache.dubbo.registry.zookeeper.ZookeeperRegistry#doRegister
publicvoiddoRegister(URL url) {try {// 调用zk客户端创建临时节点 zkClient.create(toUrlPath(url), url.getParameter(DYNAMIC_KEY, true)); } catch (Throwable e) {thrownewRpcException("Failed to register " + url + " to zookeeper " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } }到此,整个服务暴露流程就完成了。接着我们回顾一下导出全流程:
-
• 确定基础服务参数,比如ApplicationConfig,ModulConfig,ProviderConfig,RegistryConfig。。。 -
• 确定当前服务的协议列表 -
• 确定注册方式,如果有多种注册方式,则把上述的协议按照各种注册方式注册 -
• 注册过程中会判断当前服务本地是否导出,如果没有则通过DubboProtocol->Expoter->Transpoter启动NettyServer -
• 启动成功后进行注册,如果是zk,则注册到zk -
• 发送注册完成通知或调用相关的监听器进行回调
总结
重点讨论了服务导出的全流程代码,发现有时候在遇到Dubbo的SPI机制在全流程起作用的以后,跟断点都蒙圈,说明理解SPI机制不够深入,这个对于理解Dubbo框架其实非常核心。后续再继续学习下SPI,以及理解它在Dubbo整体生命周期中的作用。下篇讨论下服务的引用。
 夜雨聆风
夜雨聆风





