PageIndex再回顾:单文档场景下打败传统 RAG?
最近又看到PageIndex被刷屏了,距离上次(25年4月份的文章)关注这个项目已经过了一段时间,现在关于它的讨论越来越多,有人说是”RAG杀手”,也有人说只是概念炒作。讲道理,作为一个之前就关注过的项目,这次必须好好回顾一下,看看PageIndex到底发展得怎么样了。
RAG不需要切块向量化了?通过PageIndex构建Agentic RAG

先说说PageIndex是个啥
简单来说,PageIndex是VectifyAI搞的一个开源项目,核心思路就是:不用向量数据库,不用传统分块,用LLM推理来检索文档。
传统RAG大家都知道怎么玩:
-
把文档切成一块一块的chunks -
每个chunk搞个向量嵌入 -
扔进向量数据库 -
用户问问题时,语义搜索找相似的块 -
把这些块喂给LLM生成答案
这套路用了这么久,问题也很明显:
-
分块破坏上下文 – 一刀切下去,前后文可能就断了 -
相似≠相关 – 语义相似的东西不一定是你要的答案 -
向量数据库成本高 – 又要搭建又要维护 -
答案溯源难 – 很难追踪答案到底从哪来的
PageIndex的做法完全不同: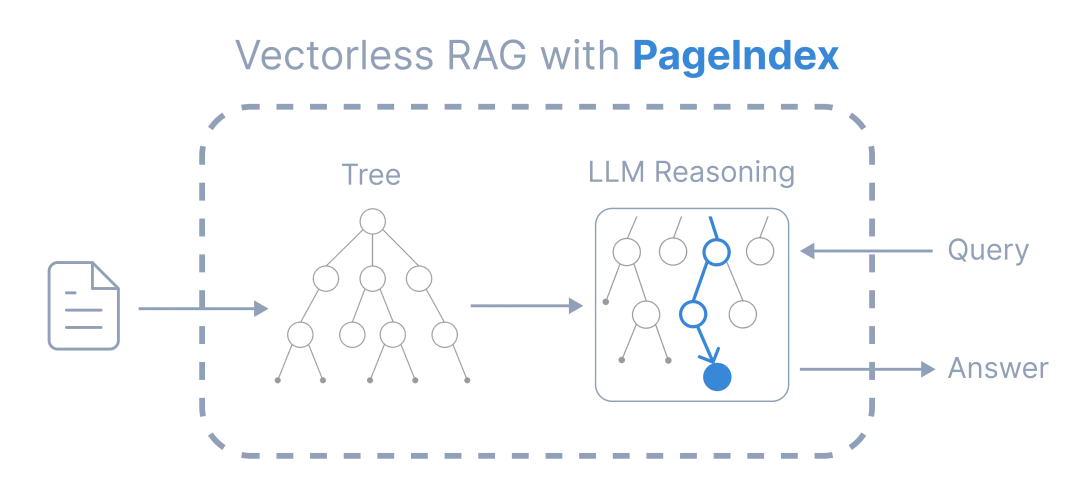
-
构建层次树索引 – 像给文档做了个语义版的目录 -
LLM推理导航 – 让模型像人一样去”翻”文档 -
保留文档结构 – 不破坏原有的逻辑关系 -
可追溯检索 – 每一步推理都能看到
根据这张信息图,PageIndex的核心特点可以总结为:
PageIndex的六大核心特点
-
Traceable & Explainable (可追溯 & 可解释)
-
基于推理驱动的检索,带有引用参考 -
每一步检索决策都能追溯来源
-
Higher Accuracy (更高准确率)
-
超越简单的语义相似性 -
关注上下文相关性而非仅仅是相似度
-
No Chunking (无需分块)
-
保留完整上下文 -
避免传统RAG分块带来的上下文丢失问题
-
No Top-K (无需Top-K检索)
-
检索所有相关段落 -
不受限于固定数量的检索结果
05 .No Vector DB (无需向量数据库)
-
没有额外的基础设施开销 -
降低系统复杂度和维护成本
-
Human-like Retrieval (类人检索)
-
像人类专家一样检索信息 -
模拟人类阅读和理解文档的方式
核心理念:PageIndex通过推理导航替代语义搜索,让大模型像人一样”读懂”文档结构并找到真正相关的内容,而不是仅仅依赖向量相似度匹配。
听起来很美好对吧?但实际情况复杂得多。
榜单确实厉害,但要看场景
PageIndex在FinanceBench上达到了98.7%的准确率,这个数字确实亮眼。不过这里有个关键点:FinanceBench测试的是单文档问答 – 每个问题都是针对一个特定的财务报告。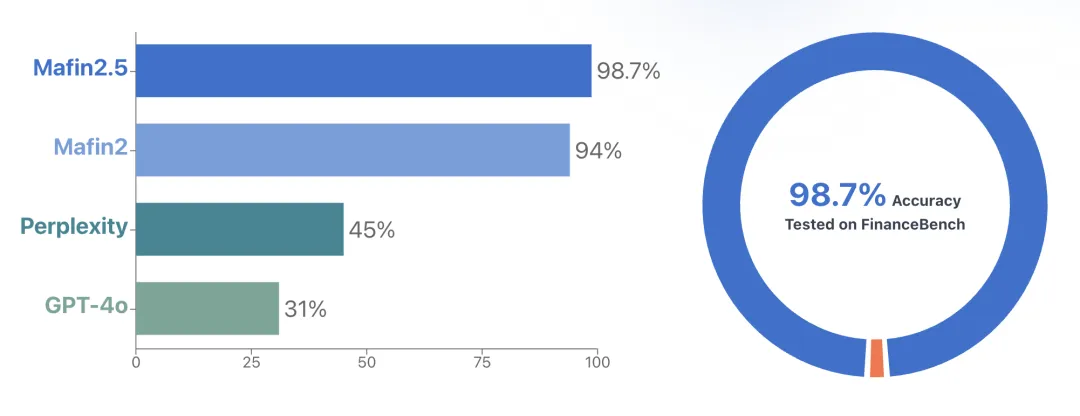
这就像让你在一本书里找答案 vs 让你在一个图书馆里找答案,难度完全不是一个级别的。
实测来了:多文档场景翻车
有人用SimpleQA-Verified数据集做了测试(约1000个问题,2795个文档),结果发现了PageIndex的一个核心问题:
当文档数量超过5个,PageIndex的树索引构建速度根本跟不上,最后不得不回退到传统的FAISS向量搜索。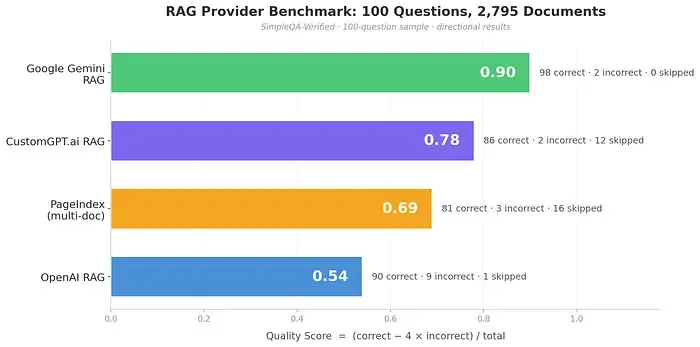
你没看错,就是它要”杀死”的那个向量RAG方法。
测试结果是这样的:
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| PageIndex | 0.69 | 96.4% |
PageIndex在回答时的准确率确实高(96.4%),但问题是它回答的问题太少了,很多时候选择保持沉默。这个4倍不正确答案惩罚的评分机制对保守系统有利,但也暴露了它在大规模场景下的局限。
PageIndex团队也很坦诚
值得尊重的是,PageIndex团队在Twitter上公开承认:
-
目前是为单文档深度分析设计的 -
超过5个文档需要其他定制技术支持 -
开源版本更多是概念验证,不是企业级系统
这种坦诚比某些项目疯狂刷榜然后不提局限性要好多了。
那PageIndex到底适合什么场景?
虽然多文档检索翻车了,但PageIndex在特定场景下确实nb:
✅ 单文档深度分析
-
财务报告审查 – 比如你要分析一份年报,找特定的数据 -
法律文件审阅 – 合同、法律备案这种结构化文档 -
技术手册查询 – 产品说明书、API文档 -
学术论文精读 – 深入理解一篇长论文
✅ 结构化文档
有清晰章节、小节、编号的文档,PageIndex的树索引能完美镜像文档结构。
✅ 高精度要求场景
PageIndex有个特点:不知道就说不知道,不会瞎猜。这对于金融、法律、医疗这种高风险领域特别重要。你宁可它说”我不确定”,也不希望它给你一个错误答案。
✅ 可审计性需求
每个检索决策都可追溯 – 考虑了哪些树节点,选择了哪些,为什么选。这对合规性要求高的场景很有价值。
实际上手:怎么用PageIndex
本教程展示如何使用 PageIndex 进行文档索引和基于推理的检索问答。
Step 0: 准备工作
0.1 安装 PageIndex
%pip install -q --upgrade pageindex0.2 设置 PageIndex 客户端
from pageindex import PageIndexClientimport pageindex.utils as utils# 从 https://dash.pageindex.ai/api-keys 获取你的 API keyPAGEINDEX_API_KEY = "YOUR_PAGEINDEX_API_KEY"pi_client = PageIndexClient(api_key=PAGEINDEX_API_KEY)0.3 设置 LLM
选择你喜欢的 LLM 用于基于推理的检索。本例使用 OpenAI 的 GPT-4.1。
import openaiOPENAI_API_KEY = "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY"asyncdefcall_llm(prompt, model="gpt-4.1", temperature=0):"""调用 LLM 生成响应""" client = openai.AsyncOpenAI(api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY) response = await client.chat.completions.create( model=model, messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}], temperature=temperature )return response.choices[0].message.content.strip()Step 1: 生成 PageIndex 树结构
1.1 提交文档生成 PageIndex 树
import os, requests# 你也可以使用 GitHub 仓库本地生成 PageIndex 树# https://github.com/VectifyAI/PageIndex# 下载示例 PDFpdf_url = "https://arxiv.org/pdf/2501.12948.pdf"pdf_path = os.path.join("../data", pdf_url.split('/')[-1])os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(pdf_path), exist_ok=True)response = requests.get(pdf_url)with open(pdf_path, "wb") as f: f.write(response.content)print(f"Downloaded {pdf_url}")# 提交文档并获取文档 IDdoc_id = pi_client.submit_document(pdf_path)["doc_id"]print('Document Submitted:', doc_id)输出:
Downloaded https://arxiv.org/pdf/2501.12948.pdfDocument Submitted: pi-cmeseq08w00vt0bo3u6tr244g1.2 获取生成的 PageIndex 树结构
# 检查文档是否处理完成if pi_client.is_retrieval_ready(doc_id):# 获取树结构(包含节点摘要) tree = pi_client.get_tree(doc_id, node_summary=True)['result'] print('Simplified Tree Structure of the Document:') utils.print_tree(tree)else: print("Processing document, please try again later...")输出:
Simplified Tree Structure of the Document:[{'title': 'DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Cap...','node_id': '0000','prefix_summary': '# DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning C...','nodes': [{'title': 'Abstract','node_id': '0001','summary': 'The partial document introduces two reas...'}, {'title': 'Contents','node_id': '0002','summary': 'This partial document provides a detaile...'}, {'title': '1. Introduction','node_id': '0003','prefix_summary': 'The partial document introduces recent a...','nodes': [{'title': '1.1. Contributions','node_id': '0004','summary': 'This partial document outlines the main ...'}, {'title': '1.2. Summary of Evaluation Results','node_id': '0005','summary': 'The partial document provides a summary ...'}]}, {'title': '2. Approach','node_id': '0006','prefix_summary': '## 2. Approach\n','nodes': [{'title': '2.1. Overview','node_id': '0007','summary': '### 2.1. Overview\n\nPrevious work has hea...'}, {'title': '2.2. DeepSeek-R1-Zero: Reinforcement Lea...','node_id': '0008','prefix_summary': '### 2.2. DeepSeek-R1-Zero: Reinforcement...','nodes': [{'title': '2.2.1. Reinforcement Learning Algorithm','node_id': '0009','summary': 'The partial document describes the Group...'}, {'title': '2.2.2. Reward Modeling','node_id': '0010','summary': 'This partial document discusses the rewa...'}, {'title': '2.2.3. Training Template','node_id': '0011','summary': '#### 2.2.3. Training Template\n\nTo train ...'}, {'title': '2.2.4. Performance, Self-evolution Proce...','node_id': '0012','summary': 'This partial document discusses the perf...'}]}, {'title': '2.3. DeepSeek-R1: Reinforcement Learning...','node_id': '0013','summary': 'This partial document describes the trai...'}, {'title': '2.4. Distillation: Empower Small Models ...','node_id': '0014','summary': 'This partial document discusses the proc...'}]}, {'title': '3. Experiment','node_id': '0015','prefix_summary': 'The partial document describes the exper...','nodes': [{'title': '3.1. DeepSeek-R1 Evaluation','node_id': '0016','summary': 'This partial document presents a compreh...'}, {'title': '3.2. Distilled Model Evaluation','node_id': '0017','summary': 'This partial document presents an evalua...'}]}, {'title': '4. Discussion','node_id': '0018','summary': 'This partial document discusses the comp...'}, {'title': '5. Conclusion, Limitations, and Future W...','node_id': '0019','summary': 'This partial document presents the concl...'}, {'title': 'References','node_id': '0020','summary': 'This partial document consists of the re...'}, {'title': 'Appendix', 'node_id': '0021', 'summary': '## Appendix\n'}, {'title': 'A. Contributions and Acknowledgments','node_id': '0022','summary': 'This partial document section details th...'}]}]Step 2: 基于推理的树搜索检索
2.1 使用 LLM 进行树搜索,识别可能包含相关上下文的节点
import json# 用户问题query = "What are the conclusions in this document?"# 移除文本字段,只保留结构和摘要用于搜索tree_without_text = utils.remove_fields(tree.copy(), fields=['text'])# 构建搜索提示词search_prompt = f"""You are given a question and a tree structure of a document.Each node contains a node id, node title, and a corresponding summary.Your task is to find all nodes that are likely to contain the answer to the question.Question: {query}Document tree structure:{json.dumps(tree_without_text, indent=2)}Please reply in the following JSON format:{{ "thinking": "<Your thinking process on which nodes are relevant to the question>", "node_list": ["node_id_1", "node_id_2", ..., "node_id_n"]}}Directly return the final JSON structure. Do not output anything else."""# 调用 LLM 进行树搜索tree_search_result = await call_llm(search_prompt)2.2 打印检索到的节点和推理过程
# 创建节点 ID 到节点的映射node_map = utils.create_node_mapping(tree)tree_search_result_json = json.loads(tree_search_result)# 打印推理过程print('Reasoning Process:')utils.print_wrapped(tree_search_result_json['thinking'])# 打印检索到的节点print('\nRetrieved Nodes:')for node_id in tree_search_result_json["node_list"]: node = node_map[node_id] print(f"Node ID: {node['node_id']}\t Page: {node['page_index']}\t Title: {node['title']}")输出:
Reasoning Process:The question asks for the conclusions in the document. Typically, conclusions are found in sectionsexplicitly titled 'Conclusion' or in sections summarizing the findings and implications of the work.In this document tree, node 0019 ('5. Conclusion, Limitations, and Future Work') is the mostdirectly relevant, as it is dedicated to the conclusion and related topics. Additionally, the'Abstract' (node 0001) may contain a high-level summary that sometimes includes concluding remarks,but it is less likely to contain the full conclusions. Other sections like 'Discussion' (node 0018)may discuss implications but are not explicitly conclusions. Therefore, the primary node is 0019.Retrieved Nodes:Node ID: 0019 Page: 16 Title: 5. Conclusion, Limitations, and Future WorkStep 3: 生成答案
3.1 从检索到的节点中提取相关上下文
# 获取节点 ID 列表node_list = json.loads(tree_search_result)["node_list"]# 拼接所有相关节点的文本内容relevant_content = "\n\n".join(node_map[node_id]["text"] for node_id in node_list)# 打印上下文(前 1000 字符)print('Retrieved Context:\n')utils.print_wrapped(relevant_content[:1000] + '...')输出:
Retrieved Context:## 5. Conclusion, Limitations, and Future WorkIn this work, we share our journey in enhancing model reasoning abilities through reinforcementlearning. DeepSeek-R1-Zero represents a pure RL approach without relying on cold-start data,achieving strong performance across various tasks. DeepSeek-R1 is more powerful, leveraging cold-start data alongside iterative RL fine-tuning. Ultimately, DeepSeek-R1 achieves performancecomparable to OpenAI-o1-1217 on a range of tasks.We further explore distillation the reasoning capability to small dense models. We use DeepSeek-R1as the teacher model to generate 800K training samples, and fine-tune several small dense models.The results are promising: DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B outperforms GPT-4o and Claude-3.5-Sonnet onmath benchmarks with $28.9 \%$ on AIME and $83.9 \%$ on MATH. Other dense models also achieveimpressive results, significantly outperforming other instructiontuned models based on the sameunderlying checkpoints.In the fut...3.2 基于检索到的上下文生成答案
# 构建答案生成提示词answer_prompt = f"""Answer the question based on the context:Question: {query}Context: {relevant_content}Provide a clear, concise answer based only on the context provided."""# 生成答案print('Generated Answer:\n')answer = await call_llm(answer_prompt)utils.print_wrapped(answer)输出:
Generated Answer:The conclusions in this document are:- DeepSeek-R1-Zero, a pure reinforcement learning (RL) approach without cold-start data, achievesstrong performance across various tasks.- DeepSeek-R1, which combines cold-start data with iterative RL fine-tuning, is more powerful andachieves performance comparable to OpenAI-o1-1217 on a range of tasks.- Distilling DeepSeek-R1's reasoning capabilities into smaller dense models is promising; forexample, DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B outperforms GPT-4o and Claude-3.5-Sonnet on math benchmarks,and other dense models also show significant improvements over similar instruction-tuned models.These results demonstrate the effectiveness of the RL-based approach and the potential fordistilling reasoning abilities into smaller models.和其他方案对比一下
最近AI圈子里新东西太多了,Vibe Coding、Skills、OpenClaw的概念太火爆了。PageIndex算是为数不多在改进RAG的项目。简单对比一下:
PageIndex vs 传统RAG
-
优势:保留结构、可追溯、精度高 -
劣势:单文档限制、索引构建慢、成本高
PageIndex vs GraphRAG
-
GraphRAG也在尝试保留文档关系,但用的是知识图谱 -
PageIndex的树结构更简单直接,但GraphRAG在跨文档推理上更强
PageIndex vs Reranking方案
-
Reranker是在向量检索后加一层精排 -
PageIndex是完全不同的检索范式 -
两者其实可以结合:向量粗筛 + PageIndex精读 + Reranker排序
我觉得PageIndex的未来不是”杀死RAG”,而是混合方案:
-
第一阶段 – 用向量RAG做文档发现,从几千个文档里快速定位到最相关的5-10个 -
第二阶段 – 对这些候选文档用PageIndex做精确提取,保证答案质量 -
分场景选择 – 单文档深度分析直接上PageIndex,大规模检索用传统RAG
这种粗筛+精提的组合拳,既能解决规模问题,又能保证答案质量。实际上已经有团队在这么干了。把PageIndex当成RAG管道的最后一环,专门负责”读懂”筛选出来的文档,效果确实比纯向量检索好不少。
最后说两句
如果你想基于PageIndex做点东西,这些方向值得试试:
增强版功能
-
支持Markdown文档(现在主要是PDF) -
多索引管理和版本控制 -
查询缓存机制(避免重复推理) -
可视化的索引树浏览器
混合架构
-
前端用向量检索做初筛 -
后端用PageIndex做精确提取 -
根据文档类型自动选择策略
领域定制
-
针对特定行业(金融/法律/医疗)优化提示词 -
训练领域特定的索引策略 -
集成行业知识库
突然发现前段时间做的关于论文问答的Agentic RAG应用和PageIndex原理不谋而合,针对论文我们输入一个问题,比如论文的实验式怎么设计,这个时候我们实际用对应实验章节回答即可了。
TextIn × Agentic RAG:让大模型真正读懂学术论文
技术没有银弹,适合的才是最好的。PageIndex不是万能的,但在它擅长的领域,确实厉害。

如果你觉得这篇文章对你有帮助,别忘了点个赞、送个喜欢
>/ 作者:ChallengeHub小编
>/ 作者:欢迎转载,标注来源即可
 夜雨聆风
夜雨聆风





